Written by Orly Ravid
Now that Sundance has announced its new line up, it seems appropriate to discuss the issue of a film’s distribution after premiering or acquisition at festivals.
It is often the case that films do not get released until 6 months to a year or even more from when the film had its festival premiere…At least this is the case when traditional distribution is pursued as opposed to planning the distribution and marketing to coincide with the premiere and work off that plan accordingly.
Here are 10 reasons for the delay in time between a premiere launch at a festival and traditional distribution into the marketplace:
1. The time it takes to find buyers. These days the market cycle is longer than it’s ever been. Sometimes even a year after a festival or market, sometimes longer to sell titles. It’s a buyer’s market, so few films enjoy the pleasure of contested bidding that forces prices up and faster closings. Sundance, of course, is one of the few festivals that commands such a dynamic and more films than at most other festivals will secure distribution, at least domestically, as a result of premiering there.
2. Once a deal is closed, then there’s the contract and delivery which takes time… months sometimes.
3. Long lead times for press are required, at least four months, and that planning usually does not happen until after deal closure.
4. The distributor needs time to find open slots/appropriate slots in the calendar for theatrical – and it’s competitive out there so getting a booking takes time, and getting the right one for the film takes even more time, again, months. Sometimes even 6 months is needed to book the right theatre for the right time.. Some of the best screens are locked in well in advance.
5. Cash flow is needed to launch marketing campaigns. This can be an issue for some distributors. Recouping some revenue from previous releases will be needed in order to fund future ones.
6. Major digital outlets take several months to upload and make a film available. Cable VOD has solicitation windows. DVD and digital also require set up times and announcing the title and marketing it ahead of time so again months of planning and slotting. One wants to be strategic about release time.
7. The time of release is sometimes specific to the film. It may be theme driven and demand specific timing or it may want to avoid direct competition. Also inventory shifts in retail stores dictate the optimal time for DVD release (ie. certain times of year, like Christmas or Halloween, call for more of a certain kind of film).
8. Internal scheduling of the distributor. As you know, distributors will have other releases that they need to navigate given what their key outlets have planned.
9. Grass roots and other marketing also demand lead time.
10. Overall, the difference between DIY and traditional distribution is that in DIY, you can plan months in advance to set up the outlets and use the press attention at a festival premiere to catapult the film into the market, even if you aren’t 100% sure which festival will be your premiere. Having everything in place to pull the trigger when you get that acceptance puts you in a good position to release. In traditional distribution, the distributor cannot do advance planning and so the planning starts after the initial buzz has been created at the festival.
I know some of you have been confused or frustrated by the lag time between a festival premiere of a film and the release. Hopefully this helps to explain the matter.
Orly Ravid November 30th, 2012
Posted In: Distribution, Film Festivals, International Sales, Uncategorized
Tags: cable VOD, DVD release, film distribution, film promotion, film sales, independent film premiere, independent film release, Sundance Film Festival, theatrical release, traditional film distribution
By Sheri Candler
As a result of my recent trip to Europe to participate in the annual FERA General Assembly and Sheffield DocFest, I found some great new independent film resources I would like to share. Sometimes we get too focused on North American resources so it is good to pull in useful information from all over the world. This will be a series of posts over the next few weeks that highlight these new services. First up, Assemble
Assemble (formerly MovieSparx) is a tool for filmmakers and distributors who want to ease the headache of building audiences and selling films on the web. It is clever software that creates and manages your web-presence, gathers and tracks your audience and provides a sales mechanisms to sell your film and related products. I spoke with Founder James Franklin about how the software works.
What made you want to build this? What need did you see in the industry that wasn’t being fulfilled properly?
JF: Simply put – we felt that the vital online presence for a film was almost always a hit and miss affair. Film websites are too often rubbish and do the film a disservice.
About 8 years ago I founded a London based design studio working just for indie film projects. We ran a lot of promotional campaigns for films around the world and learnt an enormous amount over some very high profile projects. Whilst doing this, and when I would speak at festivals about what we learnt, the same questions and problems would come up from filmmakers over and over again.
The main problem was that although everyone agreed that promoting a film and finding an audience online was important and a great opportunity, the reality was that it was very time consuming, had a steep learning curve and was a prohibitively difficult and painful struggle. Just to make matters worse, the budgets were always too small for creating the necessary marketing assets and the tools available at the time had to be hacked by techies to work for an indie film. Generally the assets for each film project – website, widgets, mailing list, shop etc – would be about 70% the same as every other project and about 30% unique. But each time everyone would have to work hard to just get that 70% out the door – we and the filmmakers felt like we were constantly re-inventing the wheel. And so we decided about 3 years ago to create a web-tool that would power these elements out of the box – film website, online shop, widgets etc. It was going to be easy, efficient, flexible and beautiful. We would also pour our knowledge and experience into the system so that best practice was baked into it from the beginning. The very first release was at SXSW in 2010.
There are a few guiding principles we’ve stuck to. Firstly, that it’s always in the filmmakers interests to help promote the film direct rather than promote yet another platform – it’s all about the film project not us. Secondly, that the production team are always the most committed and passionate of advocates and with the right tools and experience can do the best job of promoting and selling the film. Lastly, we understand the importance of the film’s marketing materials /key art / branding – this is what really sells the film and is very important online. Anything we make has to work with the branding and be both functional and well designed.
What does Assemble do for productions? Walk me through the steps all along the way of a production using Assemble from conception of a film to distributing it. Are there some example films at different stages? Describe what they are doing.
JF: We provide the best possible web presence that adapts to each stage of a film. That web presence includes the film website, branded trailers & embeddable widgets, facebook apps, a shop and other important modules. Each Module is made just for film so it works exactly as you would expect out of the box. For instance, adding an award adds a laurel to the website. Each module works with the others, so the shop can appear in Facebook and the trailer for instance. Each of those modules adapts depending the stage the project is at – so in development, it makes the most of the one photo and short synopsis you often start out with. Then the modules adapt for fund-raising or crowd funding, production, festivals and finally distribution. Lastly each module adapts by country so that it can properly support different territories being at different stages – ready for download in the USA but in theatrical in Australia – without interfering with each other.
Currently the modules are:
– Website
– Blog
– Shop
– Widget / Branded Trailer
– Facebook page app
– Screenings
– Mailing List
– Sign-up for media
– Crowd-Funding support
– Gallery
– Awards and Laurels
– Reviews
There are too many features and options to go through everything in detail. But to give an example about how this this works just for film and is designed to be more efficient, take a look at the screenings module. This handles events and screenings either as part of a theatrical release or at festivals. Usually screening dates and times end up on a single page which has to be constantly updated and is hard to find or a film relies on a potential audience remembering at a later date.
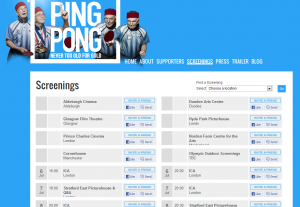
With Assemble, once the production team have entered an event or screening’s details into the back end it appears automatically, in chronological order across all assets – on the website, the trailer, in Facebook and so on. It can be automatically added to the Facebook page as an event for people to share with others. People can even send it to a friend as an invite, or share it to social networks. It can even set up a reminder for you so you’ll get an email the day of the screening. If there’s a screening near you it will flag up on the website home page. When a screening date has passed it’s automatically added to the past screenings. We can even supply a feed of data for partners.
Of course, if there isn’t a screening near you, you can demand one with a simple form or if available, you can set up semi-theatrical or community screenings and sell screening licenses. All of this works straight of the box.
We’ve also worked hard to never lose a potential customer. For instance, if someone in Canada wants to watch the film but it’s not available on DVD or for download yet, rather than giving the unhelpful message ‘this is not available in your region,’ the system will automatically work out an alternative (it may be on at a festival near them, or available from a distributor, or on Amazon – we can route them through to wherever is best). At the very worst, if it’s not available at all to them we can get them to sign up to the mailing list or demand it.
Some example sites at each stage are:
How Far Is Heaven – a simple film website
The Spirit Level – integrating with IndieGoGo
Planeat – shop with downloads and merchandise
Just Do It – powering the shop only alongside a VODO release
Black Gold – long tail of distribution (the film is from 2006)
Europe Loves Cinema – a site with a slate of films
Tigerlily Films-a production company site with many films
As the above all geo-detect, the design changes depending on where you are visiting from.
Is the software mainly built for one title at a time or for a production company in the long term?
JF: It works well for both. The system really comes into it’s own when you run a production company or distribution website and your slate of titles off the system. They all integrate together and save a lot of time and work as well as collecting all the valuable data across the whole lot. That is key, if production companies are to thrive in the
future they must take ownership of their audience data and take it with them to the next project. That way it gets easier every time. Only Assemble can make that part happen.
What advantage would it be for a filmmaker to use a distributor to access this since your site says it is for distributors as well?
JF: It’s a flexible system and so will work for both individually. Ideally, the production team should be on the system from development and running even a basic web presence from the beginning, that way they can start to take control online. And the big advantage for a production team is that our tools work with even the most complicated rights and distributor structure.
When Assemble says it builds websites, is that on the production’s own URL or is it through your platform as a 3rd party?
JF: We power websites for films, much like wordpress powers blogs. You can use your own URLs with the system. The design for each site can be done either through us as a customised project or by a third party designer. The idea is that it’s as flexible and beautiful as possible whilst still being easy.
The description says it builds an embeddable trailer. Do you mean it makes a trailer built by the production embeddable? Why wouldn’t we want this on Youtube instead where we can track views and where they come from? Does Assemble do that too?
JF: We’ve made a very flexible widget that acts as a branded trailer. We think it’s very important to use Vimeo and You Tube as part of a campaign and so we use these to provide the trailer video – You Tube and Assemble play well together. The widget then ‘wraps’ around the Youtube video to create a branded trailer which also can hold extra modules like the shop, a watch the film page, twitter feed, blog, screenings and so on. And you still get your view count up and can track who’s watching it with You Tube.
Does Assemble provide training on how to use the system? For many indie productions, this whole process of building an audience and selling directly is completely unknown so how does Assemble help demystify the process?
JF: Yes, we provide training. We’re also adding a series of how-to videos to help things. We also hope to add more general videos on how to make a success of the project using Assemble.
Does Assemble help market the projects or is it only a tool to use by film productions themselves? Would the audience ever come to Assemble or are you more a B2B?
JF: We are not another platform. We are a B2B business, we don’t want to build a relationship with a project’s audience, rather we provide the tools to enable the production team to do that. However, we do help market projects in various ways and we can advise on how to do this as we’ve many years experience at this. One of the key ways a film can market itself online is firstly through social media sharing and secondly affiliate networks.
Assemble heavily supports sharing with social media and building an affiliate network. We help advise people if needed on how to make both of these work hard for a film project. For example, we have by far the most flexible and innovative affiliate tracking system, you’re not tied to one rate and can offer different percentage kick-backs. We find discount codes can work just as well and sometimes better. In addition, we are constantly innovating and testing, then putting what we learn back into the system.
When you say you sell downloads, what makes those downloads disabled to be reuploaded on the internet? Is there a mechanism for hampering that activity?
JF: If a project sells DVDs then these can be easily ripped too. We do review for Youtube and download links. Our own download mechanism can alert us if there are excessive downloads on a single link. We think the pricing of downloads should mean that for a potential customer, it’s easier to just buy the download rather than have the hassle of finding the torrent or download link. People who would pay generally prefer to pay honestly, thats the best way to stop piracy eating revenue.
Orly Ravid July 10th, 2012
Posted In: Digital Distribution, DIY, Facebook, Marketing, Social Network Marketing
Tags: Assemble, European independent film, film distribution, film marketing, film promotion, independent film software, James Franklin, low budget independent film, MovieSparx, selling films on the web, Sheffield DocFest