The Audacity of Hope: A Window into the Minds of Filmmakers at Independent Film Week
Next week (September 15 – 19) marks IFP’s annual “Independent FIlm Week” in NYC, herein dozens of fresh-faced and “emerging” filmmakers will once again pitch their shiny new projects in various states of development to jaded Industry executives who believe they’ve seen and heard it all.
Most of you reading this already know that pitching a film in development can be difficult, frustrating work…often because the passion and clarity of your filmmaking vision is often countered by the cloudy cynicism of those who are first hearing about your project. After all, we all know that for every IFP Week success story (and there are many including Benh Zeitlin’s Beasts of the Southern Wild, Courtney Hunt’s Frozen River, Dee Rees’ Pariah, Lauren Greenfield’s The Queen of Versailles, Stacie Passon’s Concussion etc…), there are many, many more films in development that either never get made or never find their way into significant distribution or, god forbid, profit mode.
So what keeps filmmaker’s coming back year after year to events like this? Well, the simple answer is “hope” of course….hope, belief, a passion for storytelling, the conviction that a good story can change the world, and the pure excitement of the possibilities of the unknown.
Which is why I found a recent poll hosted on IFP’s Independent Film Week website [right sidebar of the page] so interesting and so telling….in part because the result of the poll runs so counter to my own feelings on the state of independent film distribution.
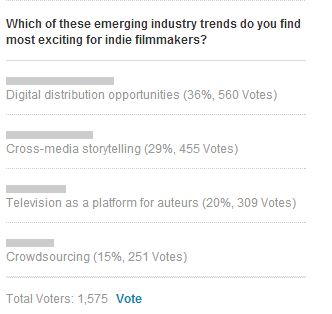
On its site, IFP asks the following question:
Before you view results so far, answer the question….Which excites YOU the most? Now go vote and see what everyone else said.
** SPOILER ALERT — Do Not Read Forward Until You’ve Actually Voted**
What I find so curious about this is in my role as a independent film distribution educator at The Film Collaborative, I would have voted exactly the other way.
I suspect that a key factor in IFP Filmmakers voting differently than I has something to do with a factor I identified earlier, which I called “the pure excitement of the possibilities of the unknown.” I’m guessing most filmmakers called the thing most “exciting” that they knew the least about. After all 1) “Crowdsourcing” seems familiar to most right now, and therefore almost routine to today’s filmmakers….no matter how amazing the results often are. 2) “Television As a Platform for Auteurs” is also as familiar as clicking on the HBO GO App….even despite the fact that truly independent voices like Lena Dunham have used the platform to become household names. 3) Cross Media Story Telling remains a huge mystery for most filmmakers outside the genre sci-fi and horror realms….especially for independent narrative filmmakers making art house character-driven films. It should be noted that most documentary filmmakers understand it at least a little better. And 4) Digital Distribution Opportunities…of course this is the big one. The Wild West. The place where anything and everything seems possible…even if the evidence proclaiming its success for independents STILL isn’t in, even this many years after we’ve started talking about it.
But still we hope.
From our POV at The Film Collaborative, we see a lot of sales reports of exactly how well our truly independent films are performing on digital platforms….and for the most part I can tell you the results aren’t exactly exciting. Most upsetting is the feeling (and the data to back it) that major digital distribution platforms like Cable VOD, Netflix, iTunes etc are actually increasing the long-tail for STUDIO films, and leaving even less room than before for unknown independents. Yes, of course there are exceptions — for example our TFC member Jonathan Lisecki’s Gayby soared to the top of iTunes during Gay Pride week in June, hitting #1 on iTunes’ indie charts, #3 on their comedy charts, and #5 overall—above such movie-star-studded studio releases as Silver Linings Playbook and Django Unchained. But we all know the saying that the exception can prove the rule.
Yes, more independent film than ever is available on digital platforms, but the marketing conundrums posed by the glut of available content is often making it even harder than ever to get noticed and turn a profit. While Gayby benefited from some clever Pride Week-themed promotions that a major player like iTunes can engineer, this is not easily replicated by individual filmmakers.
For further discussion of the state of independent digital distribution, I queried my colleague Orly Ravid, TFC’s in house guru of the digital distro space. Here’s how she put it:
“I think the word ‘exciting’ is dangerous if filmmakers do not realize that platforms do not sell films, filmmakers / films do.
What *is* exciting is the *access*.
The flip side of that, however, is the decline in inflation of value that happened as a result of middle men competing for films and not knowing for sure how they would perform.
What I mean by that is, what once drove bigger / more deals in the past, is much less present today. I’m leaving theatrical out of this discussion because the point is to compare ‘home entertainment.’
In the past, a distributor would predict what the video stores would buy. Video stores bought, in advance often, based on what they thought would sell and rent well. Sure there were returns but, in general, there was a lot of business done that was based on expectation, not necessarily reality. Money flowed between middle men and distributors and stores etc… and down to the sellers of films. Now, the EXCITING trend is that anyone can distribute one’s film digitally and access a worldwide audience. There are flat fee and low commission services to access key mainstream platforms and also great developing DIY services.
The problem is, that since anyone can do this, so many do it. An abundance of choice and less marketing real estate to compel consumption. Additionally, there is so much less of money changing hands because of anticipation or expectation. Your film either performs on the platforms or on your site or Facebook page, or it does not. Apple does not pay up front. Netflix pays a fee sort of like TV stations do, but only based on solid information regarding demand. And Cable VOD is as marquee-driven and not thriving for the small film as ever.
The increasing need to actually prove your concept is going to put pressure on whomever is willing to take on the marketing. And if no one is, most films under the impact of no marketing will, most likely, make almost no impact. So it’s exciting but deceptive. The developments in digital distribution have given more power to filmmakers not to be at the mercy of gatekeepers. However, even if you can get into key digital stores, you will only reach as many people and make as much money as you have marketed for or authentically connected to.”
Now, don’t we all feel excited? Well maybe that’s not exactly the word….but I would still say “hopeful.”
To further lighten the mood, I’d like to add a word or two about my choice for the emerging trend I find most exciting — and that is crowdsourcing. This term is meant to encompass all activities that include the crowd–crowdfunding, soliciting help from the crowd in regard to time or talent in order to make work, or distributing with the crowd’s help. Primarily, I am going to discuss it in terms of raising money.
Call me old-fashioned, but I still remember the day (like a couple of years ago) when raising the money to make a film or distribute it was by far the hardest part of the equation. If filmmakers work within ultra-realistic budget parameters, crowd-sourcing can and usually does take a huge role in lessening the financial burdens these days. The fact is, with an excellently conceived, planned and executed crowdsourcing campaign, the money is now there for the taking…as long as the filmmaker’s vision is strong enough. No longer is the cloudy cynicism of Industry gatekeepers the key factor in raising money….or even the maximum limit on your credit cards.
I’m not implying that crowdsourcing makes it easy to raise the money….to do it right is a whole job unto itself, and much hard work is involved. But these factors are within a filmmaker’s own control, and by setting realistic goals and working hard towards them, the desired result is achieved with a startling success rate. And it makes the whole money-raising part seem a lot less like gambling than it used to….and you usually don’t have to pay that money back.
To me, that is nothing short of miraculous. And the fact that it is democratic / populist in philosophical nature, and tends to favor films with a strong social message truly thrills me. Less thrilling is the trend towards celebrities crowdsourcing for their pet projects (not going to name names here), but I don’t subscribe to a zero-sum market theory here which will leave the rest of us fighting over the crumbs….so if well-known filmmakers need to use their “brand” to create the films they are most passionate about…I won’t bash them for it.
In fact, there is something about this “brand-oriented” approach to crowdsourcing that may be the MOST instructive “emerging trend” that today’s IFP filmmakers should be paying attention to…as a way to possibly tie digital distribution possibilities directly to the the lessons of crowdsourcing. The problem with digital distribution is the “tree-falls-in-the-forest” phenomenon….i.e. you can put a film on a digital platform, but no-one will know it exists. But crowdsourcing uses the exact opposite principal….it creates FANS of your work who are so moved by your work that they want to give you MONEY.
So, what if you could bring your crowdsourcing community all the way through to digital distribution, where they can be the first audience for your film when it is released? This end-to-end digital solution is really bursting with opportunity…although I’ll admit right here that the work involved is daunting, especially for a filmmaker who just wants to make films.
As a result, a host of new services and platforms are emerging to explore this trend, for example Chill. The idea behind this platform (and others) is promising in that it encourages a “social window” to find and engage your audience before your traditional digital window. Chill can service just the social window, or you can choose also to have them service the traditional digital window. Crowdfunding integration is also built in, which offers you a way to service your obligations to your Kickstarter or Indiegogo backers. They also launched “Insider Access” recently, which helps bridge the window between the end of the Kickstarter campaign and the release.
Perhaps it is not surprising therefore, that in fact, the most intriguing of all would be a way to make all of the “emerging trends” work together to create a new integrated whole. I can’t picture what that looks like just yet…and I guess that is what makes it all part of the “excitement of the possibilities of the unknown.”
Jeffrey Winter will be attending IFP Week as a panelist and participant in the Meet the Decision Makers Artists Services sessions.
Jeffrey Winter September 12th, 2013
Posted In: crowdfunding, Digital Distribution, DIY, Film Festivals, iTunes, Long Tail & Glut of Content, Marketing
Tags: cable VOD, cross media storytelling, crowdfunding, Crowdsourcing, digital film distribution, Gayby, hope, IFP, Independent Film Week, iTunes, Jonathan Lisecki, Netflix, Orly Ravid, The Film Collaborative
A Creator’s Guide to Transmedia Storytelling-interview with Andrea Phillips
Written by Sheri Candler
This week’s post should help those who are thinking about giving transmedia/cross platform storytelling a try. Andrea Phillips first encountered cross platform storytelling over a decade ago and has been writing in the space since 2005 as a full-time, free-lance transmedia author. She worked on the interactive treasure hunt Perplex City, HBO’s immersive online sensory experience The Maester’s Path for its show Game of Thrones, and with musician Thomas Dolby on an online experience for his concept album, a community-based web game based on Dolby’s entire discography called A Map of the Floating City.
I interviewed her upon the release of her new book A Creator’s Guide to Transmedia Storytelling: How to Captivate and Engage Audiences across Multiple Platforms and asked about the differences between this form of storytelling and more traditional forms, whether this takes a different skill set and how she sees this field evolving over time.
SC: Are there different principles of storytelling for transmedia?
AP: Yes and no. The basics of telling a good story are going to be the same no matter what medium you are using, but if you are going into a big transmedia project, you have to leave things more open ended than you would traditionally. You have to give yourself opportunities to extend the story late and more places where things aren’t answered, more loose ends.
In the book, I talk a lot about Chekhov’s gun, that traditional storytelling principle where if you have a gun on the mantle in the first act, then it has to be fired. (ed note: from Wikipedia: Chekhov’s gun is a literary technique whereby an apparently irrelevant element is introduced early in the story whose significance becomes clear later in the narrative. The concept is named after Russian playwright Anton Chekhov. The phrase “Chekhov’s gun” is often interpreted as a method of foreshadowing, but the concept can also be interpreted as meaning “do not include any unnecessary elements in a story.”) But in transmedia, this isn’t a good technique because you want to put lots of things in the story like this, you may need something later to use and, if it has been precedented, you can build on it.
There are lots of things in transmedia that go against the idea that the story will unfold 100% the way you envisioned. Sometimes the audience won’t react to something the way you expected them to and one of the fantastic things about working in digital media is the ability to adapt to the reaction you are getting. In films, studios do test screenings and change the ending if the audience reaction is poor or not what is desired. With an interactive narrative, you actually have a chance to change the whole story if it is playing out differently than you had envisioned. If the protagonist is portrayed as unsympathetic, you can either change the story or use that info to help him get what’s coming to him. It’s really fun stuff!
SC: Some storytellers might say “I have my whole vision for a story and I don’t want to constantly evolve it.” Is there a mindset change to this kind of work as well?
AP: “There can be, but let’s step back. There should be wiggle room, but it doesn’t have to be the whole story. The classic story of Hamlet doesn’t become a better play if you let the audience vote on the ending. You don’t necessarily want your audience deciding what the story is, but if you give them even the feeling that they have a part in influencing the outcome, it is a very powerful tool for participation. They have an investment in the story just as much as the author does.
SC: The main component I see in this is making the story interactive. The difference between the traditional way and the interactive world that we live in now is the ability to have participation rather than passively watching or reading what is put in front of you. Do you think that when we talk about educating audiences or drawing them in to the storytelling, does it depend on their age or their mindset or their history of playing video games or collaborating with other people? Is there an audience boundary that is keeping this from getting bigger? Or will this just evolve over time as we see more of these kinds of projects?
AP:”I think there are some audience boundaries, but also context boundaries. Sometimes you just want to sit quietly and read a book and not have to click on something or go look something up later. Sometimes people will want a single medium story and that will probably always be the case. The trick is to provide that single medium experience for the audience who still likes that, while identifying the audiences that want to be more engaged with the story. It is surprising, it doesn’t always have to do with age or gender or tech savvy. First find the audience that really loves your story and once you have a fandom, or base of supporters who really love the stories you tell, they will want whatever you can give them. Digital media winds up being a fairly cost effective thing to give them more of the story. It is much cheaper to roll out a social media footprint than it is to make subsequent films for instance. You are still giving them things that they want that will keep them involved in your story, until you do have the ability to get that second film, or subsequent project out.”
SC: What kind of budget considerations are we talking about when one wants to make a transmedia project? Does it mean you have to have the budget of The Dark Knight Rises or Prometheus or The Hunger Games? Or can one do it with some simple tools and elbow grease?
AP: “You definitely can do it with simple tools. The Alternate Reality Game community (ARG) is a group of fans who have gotten together to make experiences for each other out of pocket change and love. You don’t need a Dark Knight budget to make a transmedia experience. Social media tools like Facebook, Twitter, Tumblr are relatively free, shooting video isn’t free, but if you are already shooting a film, just adding on additional videos probably isn’t going to be so expensive. It is the sort of indie spirit thing as any other indie art project would have.”
SC: I hear indie filmmakers say “OK, I’m going to have a film. And then I’ll think about all of those other story aspects because those are more of the marketing or promotional efforts that come later.” Or they only see this effort as something that will fill the theater or sell DVDs. Is this a good idea or should it be planned from the start so that it is all incorporated together?
AP: “I am definitely, definitely of the opinion you should plan it all up front. Mainly because if you just tack something on later, it is going to feel tacked on. If you want it to reach its maximum power, then you have to make it all in one piece and plan for how everything will interrelate. Even from initial writing, initial conception.”
SC: In reading through some of the ideas on transmedia projects from filmmakers, I feel like some people paint themselves into a corner. These story tangents go off onto other paths and then disappear because they haven’t been clear about how it all weaves back into the overall project. Also, Lance Weiler has talked about how in his early projects, games they created to be solved by the audience in a week, only ended up taking a day and it caught the creators by surprised so they had to scramble to keep up.
AP: “This is one of the rookie mistakes that I talk about in the book. Never deploy anything unless you are ready for it to be solved. The audience is always smarter than you think it is. They are as smart as the smartest 20 people among them because they all collaborate. They will always outthink you, never think you will be smarter than your audience. Also this may come from a more marketing mindset. Some people think they will put an interesting bit of something out there, as a marketing tactic and they don’t give it much mind as to whether it leads anywhere. It gives the audience a negative feeling about your story. When you set up an expectation and then there is no payoff, it is extremely frustrating for the audience.”
SC: What do you think about all of these transmedia events, and new media funds, and new emphasis on transmedia storytelling in independent film? It seems like creators are being told this is the only way to be creating stories now. Many times these events seem a little haphazard and confusing, like they are being programmed by people who also don’t know much about this form of storytelling.
AP: “I think it is a confusing time for the creators. The audience doesn’t care about this conversation at all. They just want to know if this thing you are putting in front of them is worth their time or not. They don’t care if it is transmedia, cross media or who it was funded by. In one sense, it is an important conversation because creators have their careers to think about, but from the audience perspective, none of this is relevant if we aren’t doing good work.”
SC: Right, this is a time of experimentation. Where there is chaos, there is opportunity and you have to look a little harder for it. There is no one process that has been developed to succeed, and as an independent filmmaker, you wouldn’t want that anyway.
AP: “I had an interview with a gentleman who was very frustrated with me because he kept asking me for a blueprint on the one right way to make a transmedia project. And my answer was it depends on what you are trying to do. The book is not the one true way to create a transmedia project as much as it is a flowchart of lots of different ways. There are things you can do, and there will be trade offs to doing that. It is much less about rules than about my advice on what you can do depending on what you are trying to accomplish with your work.
The interesting thing about transmedia right now isn’t the stories, but the structures. We are in an amazing period of experimental structure and I am not sure this has happened in storytelling ever before. There has been experimental structure in individual arts such as writing with the novel, and in film. But now we are seeing this happen across all media and figuring out how to use multiple media and include the audience with digital tools in order to tell a story. The thing that fascinates me is how people fit all the elements together in their story.”
SC: As time and money are needed to create these stories, what do you see as sources for revenue? I think we shouldn’t come into this thinking if it doesn’t make millions, it isn’t worth doing. But what do you see as a way of generating revenue?
AP: “First I’d like to say that anyone who doesn’t think an artist has a right to make money is on the wrong side of history. There is no shame in commercial art. I do see some interesting things revenue wise. You for sure see the Hollywood studio model which largely depends on licensing and on selling movie tickets, a very traditional and stable way of making money.
But I also see things like Accomplice which has a live performance aspect, short, location based experiences where one buys a ticket to see it. I’ve seen The Lizzie Bennet Diaries which uses the Youtube advertising revenue stream and you can also see projects selling merchandising (posters, comics, tshirts). There’s really no limit which is the other interesting thing. Not only is the storytelling structure changing, but the business structure is too. You can hypothetically make money any way you can imagine. The question becomes how much time and money are you spending to make the project, and is it more than you could ever get in return? Knowing that only comes with experimentation and experience.”
SC: Are many film schools teaching this kind of scriptwriting/storytelling? I don’t think that many are doing this yet.
AP: Quite a number are teaching this actually. Emory, UNC, FSU, Ball State, MIT, Columbia, USC, all have programs. There is definitely an academic interest in it and especially in film schools. I am much more excited to see this being taken up by film rather than only by games. Film has been considered much more legitimate as a storytelling medium in the hierarchy of culture so transmedia is becoming much more legitimate too from its association with film.
I do think it is valuable to teach these skills to students. Film, theater, and creative writing students because it is something that exists in the world and sheer exposure is a valuable thing even if you aren’t choosing to work in it in your individual career.”
SC: Do you think this will evolve to where stories will only be told this way? I see this as a way to be in dialog with an audience and it is becoming more and more expected that the audience will be able to speak with creators. Will it be possible to say, “Oh I am not going to be in talks with the audience, I’m just going to write it as a straight book or film?” Is this really going to be an optional thing in 10 years time?
AP: “I think it will stay optional. As I said, sometimes the audience doesn’t want the whole experience. There will also be a significant number of creators who aren’t comfortable working this way or have a creative interest in not making their story interactive. I do think in the commercial space that you may not be able to get funding for your webseries or film if you don’t have a transmedia plan though. That is a reality I can very easily imagine.”
SC: In getting back to the book, tell me how it is laid out
AP: “The book is in 5 sections. The first is an introduction to transmedia. The second is an intro to storytelling. Further sections cover structure, production and then big picture which is ethics and money. The structure section is the heart of the book. I talk about considerations like using email, will you send it via your character, will the character answer? I don’t say, ‘You must use these social media outlets.’ You can’t say that, it depends on what you are trying to do and I, as the author of this book, do not know what you are trying to.
SC: Ethics, that’s an interesting section to include. What are ethical considerations to creating transmedia projects as opposed to writing a book or making a movie?
AP: “When you are putting pervasive elements into the world, things that look like they are real, you do wind up with ethical considerations. For example, a common trope is flyers for missing persons. I consider this not just ethically poor, but also bad design. As a consumer walking down the street, the first thought is not, ‘Oh my gosh, this must be part of a game or film. Let me take down this number or website and partake of this entertaining experience.’ It is probably, ‘Oh, what a terrible thing has happened. I am going to lock my doors when I get home.’ Creators need to think about the context someone will have when they happen across this material.
My favorite example I use in the book is the Parkinson’s Disease example. Let’s say you have a fictional pharmaceutical company and you make a website for it, as is the way for any transmedia project. Typically, there will be news published on this fictional pharmaceutical website. So you make some fake press release about Parkinson’s Disease, announcing the results of fake trials of a drug that improves symptoms and is expected to come to market in 3 years. Now, imagine that this website gets some Google juice and someone who suffers from Parkinson’s Disease is searching the internet for treatment options and finds this news. They make a treatment decision based on your element of fiction that was not signposted as fiction for someone who found it by accident on Google. That’s problematic because you could do harm to someone out in the world.
Many times creators don’t think about these things until something bad has happened. Things happen in the real world because of content we put out there. The world isn’t yet accustomed to questioning everything behind a story to see if it is real. All you have to do is look at how many articles from The Onion get reported as news.
My thanks to Andrea for spending time talking to me about her work and her new book. I have read the book and it is excellent, a real primer for those interested in learning more about creating interactive stories using both online tools and offline experiences. I especially liked her descriptions of World Building as it is something I don’t think creators spend enough time thinking about. World building is a good exercise whether you are creating a story structure on which to hang technology and user experiences or you are thinking through all the elements you can create and layer to immerse an audience into the world of your characters for marketing purposes, to pull them into the story experience. Every story exists in a “world” and creators should strive to bring the audience into it, let them experience it from many angles, give them something to do there, not just assume passive viewing.
For more on Andrea’s thoughts about the future of storytelling, see this video
Sheri Candler November 7th, 2012
Posted In: transmedia
Tags: A creator's guide to transmedia storytelling, A Map of the Floating City, alternate reality games, Andrea Phillips, Chekhov's gun, cross media storytelling, Game of Thrones, HBO, interactive participation, Perplex City, The Maester's Path, Thomas Dolby, transmedia, world building