All About AVOD? part 1: What To Do with Your Library Title
by David Averbach and Orly Ravid
One of the joys of working at The Film Collaborative is our extended filmmaker family. Some of the filmmakers we work with we have known for decades, back to when they made their first films. Inevitably, after seven-, ten-, or twelve-year terms, many of these filmmakers are getting their rights back from the distributors with whom they originally entered distribution deals.
They often ask us, “What is possible for my film now? What can I do to give it a second life?”
(We should state that the vast majority of these filmmakers do not have obviously commercial projects that could simply be offered to a different large streaming service like Netflix or Hulu. They are the type of films that TFC handles: solid films with good or at least decent festival pedigrees and proper distribution at the time of their initial release.)
Unfortunately, there is no one answer for every film. Nor is there a fixed answer for each type of film, as platforms’ needs can change at the drop of a hat. Except that all platforms seem to have an endless appetite for true crime docs, but we digress…
So, this blog article is less of a “how to” for library titles, and more of a “how to think” about them.
Certainly, there are non-exclusive subscription-based (SVOD) platforms that align with various content areas, such as Documentary+, Topic, Wondrium, Curiosity Stream, Coda, Qello, Tastemade, Gaia, Revry, and many more (check out our Digital Distribution Guide for more info). These are platforms that offer a revenue share based on minutes watched. Since they may have not been in existence when the filmmakers’ original distribution deals were arranged, they are definitely worth exploring when one (or more) of them is a fit for your project.
But there are also ad-supported (AVOD) platforms1, which are free to the end user and rely on commercials that play before the film starts. Generally speaking, AVOD platforms seem to be more lucrative in terms of revenue than specialized SVOD platforms, and we’ve heard that some films are making “real” money them (more on that later). While there’s no guarantee that AVOD platforms will bring in more money than SVOD platforms, or much money at all, this at least makes sense, anecdotally: with the rise in commercial streaming services and especially since the start of the pandemic, folks are watching increasingly more content, but actually spending less above and beyond the Netflix/Amazon Prime/HBO/Disney etc. combination of platforms that they have ostensibly come to view as basic utilities.2 So AVOD provides a win-win for platforms and consumers alike.
Until recently, filmmakers have been somewhat reluctant to place their films on AVOD platforms, but they are coming to realize what distributors have known for a few years now—that AVOD can continue to bring in revenue when transactional platforms such as iTunes are no longer performing for a film the way they might have at the beginning of their digital run.
So, we set out to ask what we believed was a simple question: which AVOD platforms are taking which type of library content? The Film Collaborative has some limited experience with AVOD platforms, but we felt it prudent to talk to some folks that do this day in and day out. To that end, we reached out to Nick Savva, Vice President of Content Distribution at Giant Pictures, and Tristan Gregson, Director of Licensing & Distribution at BitMAX.
The answer turns out to be a complicated one. Here’s why:
Most AVOD platforms are looking for all kinds of content. One of the trends that has been occurring for the past few years is the addition of new platforms, not just in the U.S., but globally. And the pandemic has accelerated existing trends, so there are even more new platforms than ever. These platforms are not going to be able to produce or acquire enough new content to justify their existence, so they rely on library titles as much as they do new releases. So, the good news is that there are more outlets and revenue opportunities for library titles than ever.
The not-so-great news is that sometimes AVOD platforms are actually looking for specific types of films, but only for a limited time to fill a specific need. Platforms have a good sense of what percentage of their films are, for example, comedies, dramas, thrillers, horror, documentaries, true crime, etc. When they look at who is watching what, if comedies are overperforming on the platform relative to the percentage of titles they occupy overall, the platform may not take as many comedies for a while until that changes, or they could decide to double down and take more comedies at the expense of other types of films. Conversely, if there is a category that is underperforming, they could decide that they need some fresh meat in that category, or simply decide to take less of it.3
So why exactly is this bad news? Because as the needs of AVOD platforms ebb and flow, the entities with the best chance of succeeding are those that can respond quickly to calls from these platforms for specific content. A high percentage of the work Giant Pictures does with AVOD platforms involves their distributor clients, who use Giant as a sort of white label service. Giant is tasked with placing their content libraries on these platforms because these distributors don’t have the bandwidth to keep up with which platforms want what from month to month. Similarly, BitMAX works with many studios to deliver to these platforms, but the studios are the ones handling the licensing. What this means is that the bulk of content going to AVOD platforms is coming from the content libraries of studios and distributors. That is not to say that films from individual filmmakers aren’t being placed on AVOD platforms by Giant/BitMAX, it’s just that studios and distributors are their go-to sources for content because they can provide a bunch of titles with a quick turnaround.
The sad reality here is that AVOD is one area of distribution where middlemen are being added to the mix in a way that makes it harder for individual filmmakers to take back control of their films.
Many of the filmmakers who have just gotten their rights back often remark to us how glad they are to have done so, as if they are finally getting out of a bad marriage. Even if the relationship wasn’t such a badmarriage, this sentiment—justified or not—perhaps stems from the fact that their TVOD sales had dropped over the years and they felt like their distributor was no longer doing anything for their film, or that they were tired of not receiving reporting because there were long periods of time with no earnings. The last thing they appear to want to do is start up a new relationship with a new distributor or aggregator and incur more encoding costs for a shot in the dark in terms of being accepted by these platforms only to earn $12 a quarter in earnings.
It’s important to really have a look at the reporting your old distributor provided you. There’s a good chance that simply re-creating what your old distributor did—perhaps your film was already on AVOD platforms—is going to give you a completely different outcome. But to the extent that your project has not been tested in the current landscape, what should a filmmaker be thinking about if they find themselves in the position of deciding whether to go it alone or offer their film to another distributor?
It’s Your Time and Money
Bandwidth:
Tristan Gregson remarked that the same rules apply for library titles as when just starting out, and his stance was the following: if you know how to engage your audience then put it somewhere. If not, then don’t. Whether you try to go it on your own or partner with another distributor, unless there is someone that’s going to remind your audience that it’s there, there’s a good chance your film will sit unnoticed in a glut of content. This is going to take some effort and while a new distributor might do a bit of marketing, you are going to have to get creative. Perhaps time the re-release of this older film with a new project of yours?
Cost:
If you go through an aggregator like BitMAX, you are probably looking at a bare minimum of $2,000 for encoding, QC, and delivery and to pitch and deliver to a few SVOD or AVOD platforms. It’s a fee for service, so they will be hands off when it comes to strategy, and uninvolved when it comes to your earnings. If a distributor like Giant Pictures is willing to work with you, it can cost twice that much, but they will be real partners in the sense that they will be proactive in helping you come up with a strategy. They will also take a certain percentage of your earnings. You may also be able to negotiate lower encoding costs in exchange for an increased percentage of your earnings.
What is in it for the Platform?
Metrics:
Nick Savva advises filmmakers to think about your film like a platform would: what are your film’s metrics? These scores can tell a lot about the public’s level of familiarity with your film, and there are data tracking services that distributors and platforms use to determine them. Also among the first things that an acquisitions team would look at would be indications of basic audience awareness, such as the of the number of positive reviews on Amazon, or the ratings on IMDb. If the metrics are good, a deal might be attractive to a platform. Are there any recent reviews? In other words, does your film still hold up?
Is there one Platform that is better for my film than others?
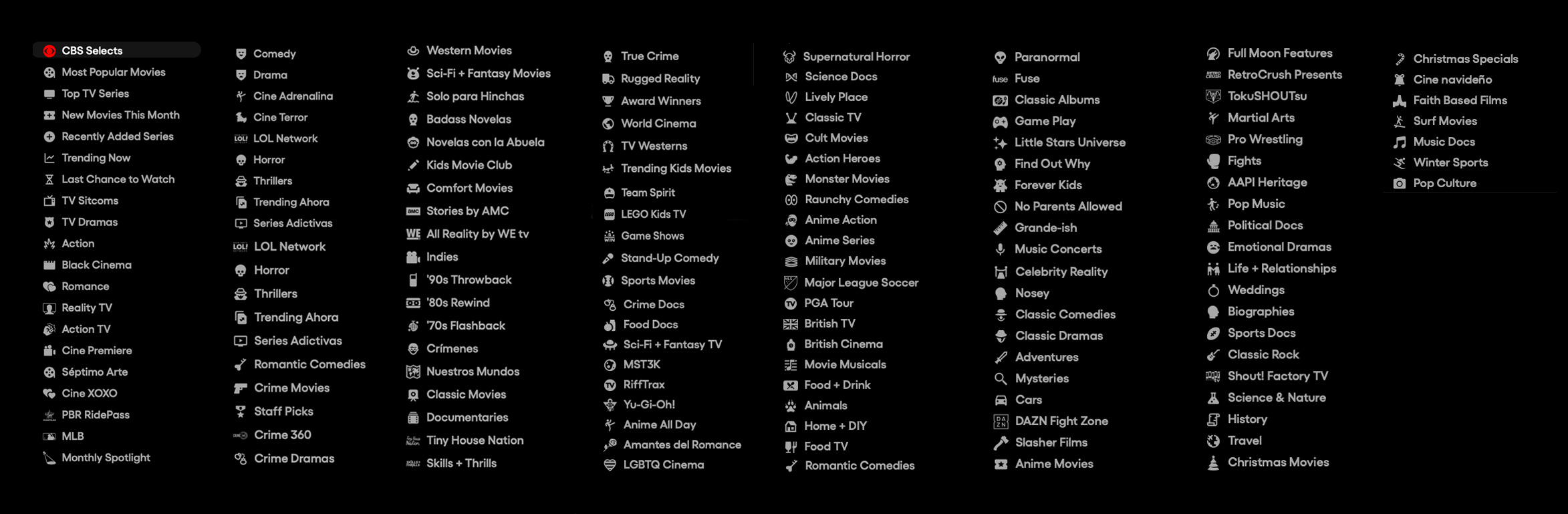
Honestly, there are not all that many AVOD platforms in the U.S. Tubi, Pluto, Roku, Peacock, IMDb TV, and a few others. The good thing about AVOD is that most deals are non-exclusive, meaning that you can be on more than one at once. But should you apply for all of them? How does one decide?
Signal Boost:
The following might not be possible for every film, but, if possible, try to think about the likely television habits of your audience and the specifics of each platform and take advantage of the free signal boost.
People are very familiar with platforms like Netflix and Hulu, but when it comes to platforms like Tubi or Pluto, why would one choose to watch one over the other? The answer might be simpler than you would think!
Does your film have a TV star in it? If they are on the FOX network, chances are that audiences will see ads for Tubi, because Fox is the parent company of Tubi. If they are on NBC, then perhaps Peacock or Xumo will be advertised.
There are also tricks that might apply for documentaries too. Pluto just became available in Latin America and Mexico, so films with Latinx content might want to consider that platform first.
One of The Film Collaborative’s digital distribution titles, The Green Girl, has been doing extremely well on Pluto, but not so well on Tubi or Roku, and for the longest time we couldn’t figure out why. Then it hit us: this documentary is about an actress who famously appeared on the 1960s television show Star Trek. Since Pluto is owned by Viacom, which is the parent company of Paramount, Pluto is the AVOD destination platform for Trekkies!
Keywords:
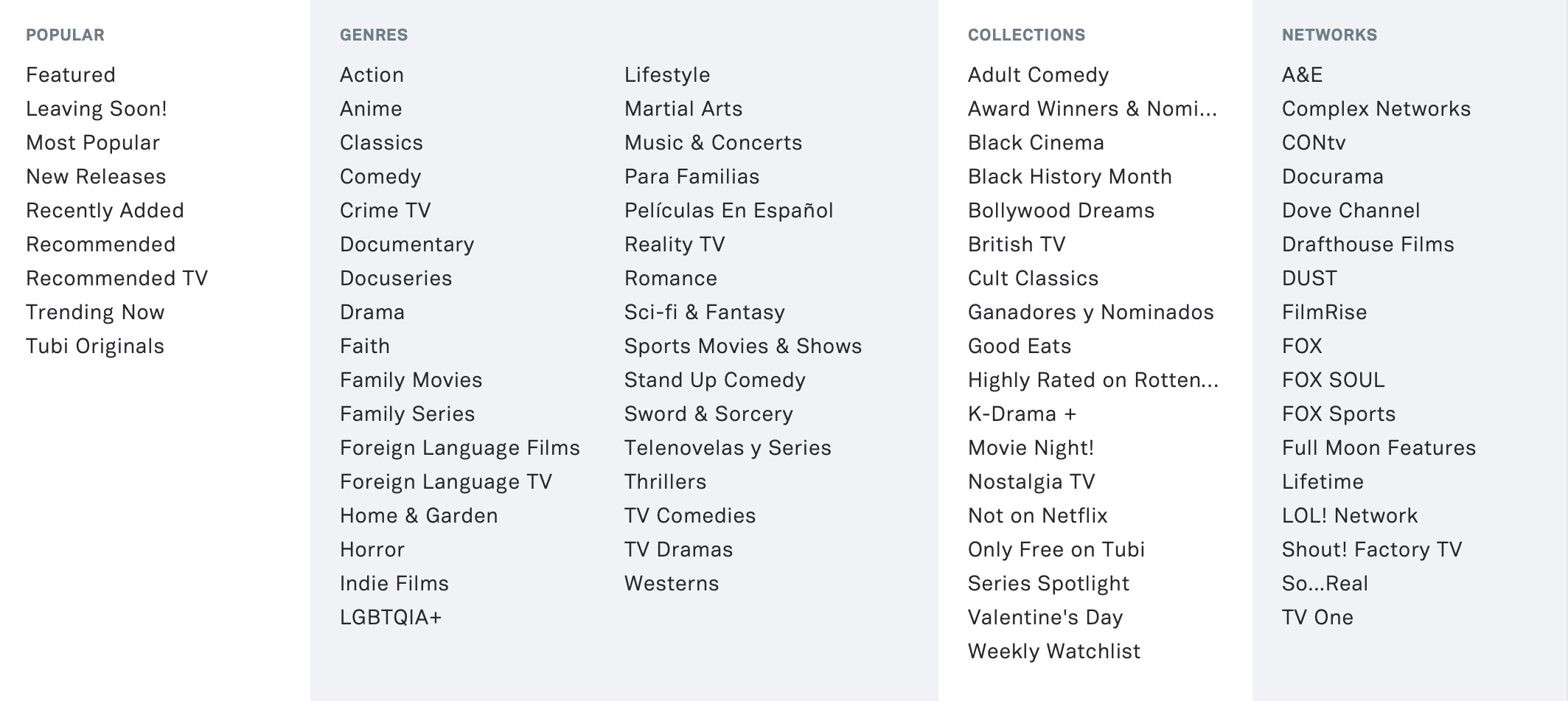
Make sure your keyword game is strong. Aggregators and distributors will ask you to fill out a metadata sheet with genres/keywords, but you must make sure the choices conform to actual categories and genres on the platforms, which can differ from one another and evolve over time. Distributors have even admitted that it’s hard for them to keep up sometimes, especially if such metadata is capture via web interface. Case in point: The Film Collaborative placed a few films we have been working with for years onto Tubi, but the keywords that we chose when we first submitted the film to our aggregator were based on iTunes genres, which are very narrow. Cut to the films getting up onto Tubi, and they were almost impossible to find without searching for their exact titles. It’s been several months, and we are still struggling, with the help of our aggregator, to get these updated on the platform. Bottom line is that it’s important to be familiar with each platform and know how one might best search for your film and be proactive to ensure that the proper information is being delivered to each platform at the time of delivery.
Pluto TV (owned by CBS/Viacom) offers a dizzying array of genres/categories to choose from (they appear in a vertical sidebar and seem to rearrange themselves periodically)
Tubi’s current “Browse” navigation tab. Tubi’s parent company is Fox Corporation.
Very Mini Library Titles Case Study
We talked to director/producer Kim Furst, whose rights to her 2014 film Flying the Feathered Edge: The Bob Hoover Project came back to her after her aggregator (Juice) declined to renew the term. She expressed that she did not want to use another aggregator like Distribber/Quiver/Bitmax/FilmHub because there was a concern that they might not be around in another 5 years. (As you probably are aware, Distribber has shuttered, and Quiver is not currently accepting films from individual filmmakers and will probably turn into something else).
So, she went with Giant Pictures.
The cost to re-encode was about $4K. While she did not feel great about having to shell out such a huge chunk of cash on a library title, Kim still felt that the film still had life in it, and she wanted to try other distribution avenues, such as public television, that she never managed to do when the film originally came out.
We should note that one of the reasons why Giant might have been interested in the film was that it is narrated by Harrison Ford. The film is about Bob Hoover, an American fighter pilot and air show aviator, and Ford has a longstanding love of flying planes. So, there is some commercial appeal that can be leveraged here.
She is at the stage where they have initiated the re-release. Right now, the film is back up on TVOD platforms, including being re-placed on Amazon, which Giant was able to accomplish despite the platform’s embargo on unsolicited non-fiction content.
We asked Kim to report back on what happens next. We suggested that she note where all of Harrison Ford’s top movies are on AVOD and take note if that platform sees any boost from the connection.
Revenue Range
With so many variables and permutations, it’s hard to give a real range in terms of what’s possible for a library title on AVOD, especially since it’s impossible to know when we are talking about the revenue of a “library” title—as opposed to that of a title that enters AVOD as part of their “new release” window.
When I asked Tristan about revenue, he acknowledged that to even talk about it would put us into “anecdotal space,” because he isn’t aware of what it took for some of his clients to earn, for example, 5 figures during an AVOD revenue period, as compared with other clients who were only able to earn, say, 3 figures. While he admitted that he has seen a single independent film title clear quite a bit, he also reiterated to me that at a certain point of revenue generation, distributors tend to get involved with a title to signal boost, so it isn’t exactly “a fair comparison to those independents working day in and day out to make a few grand on their title. But if the message is that you don’t have to be working with one of the major studios to reach seven figures in revenue, it can still very much be accomplished in this current age of VOD releasing.”
Nick spoke more specifically to AVOD, noting that they “have had a couple of indie titles which have generated $100k+ royalties in 1 month on 1 AVOD platform. But, of course, those are outliers.”
One of our filmmakers told us that they have two filmmaker friends-of-friends (whose films deal with Black Cinema content) for whom Tubi is paying well: one reported $15K a month in residuals while the other one says they are making $4-6K a month on a movie released 10 years ago. Both filmmakers allegedly went through an aggregator, but their friend said they were reluctant to allow the names of their respective films to be shared publicly.
So, as Tristan remarked, it’s best not to hold too tightly onto evidence that is merely anecdotal, because TFC certainly knows films that are making almost nothing on AVOD.
Notes:
1. As we were conceiving this article on Library titles, and realizing how important AVOD could be for an older title, Tiffany Pritchard of Filmmaker Magazine approached us about an article she and Scott Macaulay were writing about AVOD. Its title is Commercial Breaks and it is available in the January 2022 issue of the magazine (behind paywall, at least for now).
2. As a reference, this article discusses how shorter theatrical windows might be accelerating TVOD decline and shows the increase in both spending and subscription stream share from 2019 to 2021. Others, however, predict that streaming services will lose a lot of subscribers in 2022. Still, it’s hard to know how streaming services are faring, as many of them are not transparent in their total number of subscribers and average revenue per year.
3. Stephen Follows assembled a team, called VOD Clickstream, that uses clickstream data to analyze viewing patterns on Netflix between January 2016 and June 2019. He also offers a ton of information on his website. In November 2020, he presented a talk entitled, “Calculating What Types of Film and TV Content Perform Best on SVOD?”, in which he outlined how he believed Netflix navigates how popular a genre is versus what percentage of content of that genre is available on the platform.
David Averbach February 8th, 2022
Posted In: Digital Distribution, Distribution, Distribution Platforms, DIY, Documentaries, technology
What the hell is the “Blockchain” and why is everybody talking about it? (Part 1 of a 3-part series on Blockchain)
April 19, 2018 • Kathy Susca, TFC Films Manager

‘Blockchain’ is 2018’s buzziest word in regard to film distribution, so we want to make sure all of our readers are savvy to what it means, how it works, and its potential for distribution. This is the first post of 2-part blog on blockchain—in this article, we’ll define what the blockchain is, explain its technical structure, and discuss some of the possible applications for media. In part 2, we’ll discuss industry perspectives on advantages of these systems.
At its core, blockchain technology is based on a very simple concept. It is a distributed ledger system, meaning that its primary purpose is tracking transactions, like a pen-and-paper accounting ledger. ‘Distributed’ means that it is de-centralized; it is not maintained or controlled by any single authority or company. Rather, it is maintained and updated by the user base, on a peer-to-peer (P2P) basis.
The ledger is organized as a sequence of blocks (the “blockchain”), each including multiple transactions. It generally works like this:
- Any user can join the network and read all past transactions in the blockchain.
- To create a new transaction, the user signs a request and broadcasts it to the network.
- Other users can collect pending transactions, create a block and add it to the blockchain.
The special thing about blockchains is that blocks added to the chain are a permanent, verified, and public record of the history of all transactions within the system. To avoid tampering of blocks, the process of adding new blocks to the chain is made intentionally difficult: users compete to verify blocks and add them to the chain, and they are rewarded when they succeed.
In this article, we will be using Bitcoin as an example because it was the first successful large-scale implementation of a blockchain, where each block contains records of money transfers. However, blockchain technology is not limited to financial transactions—it can be used to record copyright ownership, royalty payouts, etc. It is important to understand that blockchain technology is just a method of recording data and verifying its existence at a certain point in time; different systems that we will discuss later in this article all employ their own unique implementation of these concepts.
Because of cryptocurrency’s prominence at the moment, there is a wealth of information available for further reading. The New York Times recently posted an excellent animated video with a basic explanation of cryptocurrency. Using Bitcoin as a lens, we can start to understand blockchain systems, their uses, and their limitations.
Hash functions are a key element of blockchains: they are used to “chain” blocks together and to verify their contents. A hash function generates a unique numeric ID from the data of an input block, like a fingerprint. If even one character is changed in the input data, the resulting hash can change entirely: this makes it very difficult to alter input data and get the same fingerprint. Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 hash function: you can try to enter some text here and see how the resulting hash changes if one character is altered.
Hash functions play two roles in the blockchain: linking a new block to the previous one and controlling the creation rate of new blocks.

from BraveNewCoin.com’s introduction to Blockchain technology
Linking new blocks to previous ones: Each block contains the fingerprint (hash) of the previous block. See the illustration above: when a block is added to the chain, it links itself to the chain by including the prior block’s fingerprint in addition to pending transactions. In this way, each block’s fingerprint is dependent on the chain of all blocks coming before it. Therefore, each block’s hash is a fingerprint for the history of the entire chain.
Controlling the creation rate of new blocks: In Bitcoin, blocks are added to the chain when they are “mined,” and users can earn money for mining blocks. To mine a block, miners must add a mystery number to the block, to make its hash start with a required number of zeroes. Given that hash functions are, by design, almost impossible to reverse-engineer, the only effective way to mine a block is to simply keep plugging in different values for the mystery number until it works. Once a block is mined, it is broadcast to the network and it becomes part of the blockchain, together with all of its transactions, and additional transactions rewarding the miner with new Bitcoins and transaction fees. There are server farms doing this lucrative work, all day every day.
One of the main points of a blockchain system is to do away with a potentially fallible central authority overseeing the record keeping. Thus blockchains are necessarily public – at least to the users on that system. The monetary rewards coming from mined blocks are how the Bitcoin system motivates its users to participate in processing transactions and adding them to the blockchain. But how does the system guarantee that recorded blocks are trustworthy, that a transaction won’t be removed or altered, creating an alternative history of recorded transactions?
Well, imagine that two blocks are added to the chain at exactly the same moment, creating two competing branches of the blockchain (this is called “forking”). As each chain grows, how does the network decide which one is the official record? The longer chain wins, and the transactions in the shorter fork go back into the pool of pending transactions. A transaction isn’t considered ‘confirmed’ until it is several blocks back in the chain, and therefore unlikely to be in a forked chain that will be dissolved. It currently takes about 10 minutes for a block to be mined, so transactions are considered ‘confirmed’ after about an hour (6 blocks). As the chain gets longer, the individual blocks (and the records they contain) become more and more secure.
To tamper with a block that is already in the chain, it would be necessary to do the difficult work of re-mining that block, and all the other blocks after it, in order to create a forked chain that is longer than the original chain. Meanwhile, other miners would be adding blocks to the original chain, making it longer and longer. In order to beat the rest of the network (working on the legitimate fork), a malicious user would have to implement what is known as a“51% attack”—to control 51% of the mining power in the entire network to have a statistically likely chance of mining several blocks in a row. Since having 51% of the hashrate is prohibitive both logistically and financially, and even then the success of the attack would not be guaranteed, users stand to make more profit by protecting and securing the blockchain.

Blockchain systems use a variety of methods to determine the probability of a user/node being the next one to add a block, but by far the most popular method is “Proof of Work.” In this system, a user’s hashrate (how many hashes they can compute, per second) determines their likelihood to mine the next block. Server farms, for instance, are more likely to mine a block quickly than an individual user. This is the system used by Bitcoin that we’ve been describing so far. Other systems are Proof of Stake (a lottery based on how much commodity a user owns), Leased Proof of Stake (users pool their commodities and share earnings), Delegated Proof of Stake (users elect nodes), and Proof of Importance (‘worthy’ users are selected). In each of the systems above, the users are financially motivated to maintain the integrity of the system, whether the benefit is direct, indirect, or collective.
This necessarily-public nature of the blockchain carries with it some privacy concerns for the users. All transactions a user engages in are publicly available, and therefore traceable. Anybody with access to the blockchain records is able to reconstruct a user’s entire history of transactions (and therefore discover their account balance). If that user is successfully identified as a specific person or entity, their privacy has now been compromised.
With Bitcoin, this problem has been tackled through the use of addresses – unique alpha-numeric identifiers linked to a user’s account. Each user can have multiple addresses, and it is standard practice to create a new one for each transaction in order to ensure privacy of both parties. When used properly, addresses can anonymize transactions.
Copyright Management: A blockchain system would be ideal for verifying who owns the copyright on a piece of intellectual property at any given point in time. Any sale of rights could potentially be recorded and accessible to the public. Furthermore, quoted in Information Week, Tiffany Li of the Yale Law School’s Information Society Project says, “Technically, one could imagine generating a hash for every piece of intellectual property you would like to identify as your creation and using a public blockchain-based registry to authenticate ownership of IP.” Other experts point out that integrating the new blockchain copyright management systems to work seamlessly with ‘legacy systems’ would be a complex, costly, and years-long process. However, some companies have already begun this work, like Po.et.
Royalty tracking and payouts: In a system in which media is created by more than just a single artist and distributed across a variety of platforms worldwide, royalty payments can become very complex. Blockchain Royalty Corp is one company doing this type of work in the music industry, and their system integrates smart contracts to automate the process and ensure that payouts are done accurately. The Open Music Initiative takes the idea of royalty tracking to the next level, by designing a system that also helps fans discover other works the artists are credited on.
Crowdfunding: iProdoos will allow the users of the platform to “decide what content is made and available on the iProdoos platform and how long that content lives”—essentially they’re crowdsourcing programming via crowdfunding on the blockchain. Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are a way to raise funds for a startup by pre-selling your cryptocurrency to investors. This type of model could be applied to fundraising for a film project, and facilitating paying back the investors using the blockchain records.
Direct Distribution: Creators could potentially use blockchain technology to track transactions. However, the content itself would likely have to be stored and distributed using a different platform, as the blockchain is not intended to store large amounts of data like a video file. One potential path would be to integrate blockchain verification with BitTorrent P2P technology, in which media is shared directly between users and the dissemination of the files is crowd-based. Like blockchain technologies, BitTorrent negates the need for a central company or figure to maintain records or even be involved in transactions beyond providing the platform. IPFS seeks to replace the current HTTP web with a decentralized P2P system (that employs hash functions to identify information in nodes)—ideal for saving bandwidth when sharing large files. Decent, Lightstreams, Treeti, White Rabbit, Cinezen, SingularDTV, Stream Space, and Vevue for example, are just a few of the companies already focusing on this type of distribution.
Some hurdles to consider: We’ve spent a lot of time discussing how users in Bitcoin are motivated to participate in the upkeep of the system. In decentralized systems, users must be incentivized, and a non-cryptocurrency-based system (that cannot necessarily offer financial incentives) complicates that issue. The public vs. private tension must be resolved as well—if a copyright attribution is anonymous, what good does it do? We have also discussed data storage concerns for large media files. Furthermore, while the blockchain may in itself be a secure ledger system, the peripheral systems that make it practical for use (data storage, cryptocurrency wallets, file encryption, smart contracts, etc.) are not necessarily as invulnerable as the blockchain itself. Finally, cryptocurrencies using blockchain technology aren’t necessarily well-suited to microtransactions due to transaction fees, so setting up royalty payouts on individual consumer purchases as they happen would be cost-prohibitive.
Kai Stinchcombe, a prominent critic of blockchain technology points out that “ten years in, nobody has come up with a use for blockchain,” and goes on to detail the lack of recourse if you are defrauded in these systems, as well as the overall clunkiness of the technology in comparison to centralized systems. In a subsequent article, the same author writes, not without reason, “Blockchain systems do not magically make the data in them accurate or the people entering the data trustworthy, they merely enable you to audit whether it has been tampered with.” We are just scratching the surface here, but these are conversations that must be had if artists are going to monetize their work using these new technologies.
Of course it is not possible to know what the future will bring, but let’s imagine these hurdles are all surmountable, that you could integrate the above technologies (Cosmos for example facilitates interoperability between blockchain systems). Then, you could develop a system that brings together copyright management, royalty payouts, direct-to-consumer-sales, distributed storage of media, and smart contract functionality; a system with completely decentralized, direct distribution and rights management that is functional across all cryptocurrencies. That would be a real media revolution—and it may not be too far off.
Keep an eye out for the second part of our series on the blockchain, in which we explore some entertainment industry perspectives on the advantages that blockchain technology can bring to some of the more challenging pieces of film distribution that we currently have.
How Bitcoin Mining Works
Bitcoin Wiki
Blockchain: What Business Leaders Need to Know About This Disruptive Technology
Blockchain Technology Moving Into Cable, Advertising Sectors
Can Blockchain Technology Solve Copyright Attribution Challenges of Digital Work?
Film Slate To Be Financed by Digital Currency and Distributed Via Blockchain
What is Blockchain and How Will It Change the World?
How Blockchain Could Start To Make Waves in Media and Entertainment in 2018
Betting on the Bitcoin Blockchain
Kathy Susca April 19th, 2018
Posted In: blockchain, Blockchain, Digital Distribution, Distribution, privacy, technology