Distribution roundup from SXSW 2013
HELLO SXSW! It’s hard to believe that it’s been a whole year since SXSW 2013. The film festival (and all the other things that happen) has consistently been on the cutting edge of distribution options. It is truly a one of a kind festival for a number of reasons and while they won’t pay for filmmaker travel, they do provide huge opportunity for the savvy filmmaker.
With 125+ films and the literally hundreds of panels, it can be daunting trying to get the attention of eyeballs. That said, over 2/3 of the films that world premiered here last year have secured some form of domestic distribution (on par with Tribeca and second only to Sundance).
The Film Collaborative world premiered I Am Divine at the festival last year and our release strategy is a prime example of how the fest can be a launching pad. The film went on to play over 200 festivals in less than a year (more than any other film in the world) racking up screening fee revenue. TFC also managed its theatrical release starting last October. The entire operating budget for the theatrical release was less than $10k and the film has grossed over $80,000 theatrically to date. As impressive as that is, the festival revenue surpassed the theatrical total. Meanwhile, despite never paying for a single print ad, we just passed our 50th theatrical engagement. The film has almost 40,000 Facebook Fans and will be released on DVD/Digital in April through Wolfe Releasing, and a TV premiere is scheduled for October.

SXSW produced two clear narrative breakouts last year, neither from a first time filmmaker. Joe Swanberg’s Drinking Buddies was a day and date release and managed to gross $300k+, his highest grossing film to date. It has chartered quite well on iTunes and other digital platforms and is likely quite profitable for Magnolia (hence why they acquired Swanberg’s follow up out of Sundance this year).
The other narrative breakout was the critically acclaimed Short Term 12. Sundance’s loss was SXSW’s gain and the film grossed over $1 million at the US Box Office, won multiple audience and jury awards and is the highest grossing film ever for Cinedigm. The film has been in theaters non stop for over ½ a year!
12 O’Clock Boys was released day and date and is Oscilloscope’s highest grossing release in over a year. It also topped iTunes and, to date, the film has managed over $80k in revenue. In fact, the day and date strategy has not appeared to hurt other top performing SXSW Docs.
Magnolia grossed $138k with Good ‘Ol Freda Also passing the $100k mark was Spark: A Burning Man Story. The film managed over $120k with a self financed theatrical handled by Paladin. What stood out wasn’t the total, but the fact that 70%+ came from Tugg Screenings! FilmBuff handled the digital rights where the doc performed equally as well. Meanwhile IFC’s The Punk Singer was a more standard release, but still a solid success passing the $120k gross mark.
Fall and Winter, Euphonia and Some Girls all opted for digital releases via the newly established Vimeo on Demand service. This year, Vimeo is investing $10,000,000 into its service and offering $10,000 minimum guarantees in exchange for an exclusive digital distribution window to any film that has premiered at one of the 20 leading global film festivals throughout 2014. Filmmakers also may apply for marketing support. The huge thing though is that the filmmaker gets to keep 90% of the revenue, which is far better than any other notable digital platform.
Also popular amongst the filmmakers was FilmBuff. No fewer than eight world premieres were distributed digitally by them. A few of those films also had small DIY theatrical releases.
It should be noted that DIY releases cost money which might be a problem for those who did not budget ahead of time for such a release. However, cash strapped filmmakers have raised DIY funds via Kickstarter to aid in such releases. TFC helped Big Joy: The Adventures of James Broughton raise over $50k. Loves Her Gun, This is Where We Live, and Love and Air Sex (AKA The Bounceback ) all raised distribution funds via crowdfunding.
Netflix took The Short Game as their first documentary acquisition and the film had a modest theatrical run via The Samuel Goldwyn Company. Pantelion passed $50k with Hours which has been a top digital performer following the death of its star, Paul Walker. First Run Features is approaching $40k with Maidentrip and companies like IFC, Magnolia, Oscilloscope, Breaking Glass, FilmBuff, and Variance all took multiple films.
On the TV side, SXSW films have premiered on Al Jazeera, CNN, Showtime, PBS, and VH1. Many of those films had some form of theatrical too. Documentaries continue to be the bulk of the festival highlights though the top two grossing films were narratives. The festival is second only to Sundance for world premiering a doc.
As we look to what the 2014 crop will offer, there are already some game changing situations. BFI is repeating their marketing match offer of up to $41k for any distributor who acquires one of their five UK based SXSW premiere films for distribution. As pointed out earlier, Vimeo’s offer extends beyond SXSW to 19 other upcoming festivals. I encourage you to keep an open mind and craft your film strategies now! The $10K MG that Vimeo offers for such a short exclusive digital window (plus you get to keep 90% of any revenue after the MG is recouped!) is better than many advance offers made by lower profile distributors. You can always pull your title off after the MG is recouped and seek more traditional distribution routes as Cinemanovels did out of Toronto last year.
SXSW is a great place to showcase your film, but without a formal market and with all the craziness that surrounds the festival from the interactive and music sides, it is unlikely that seven figure deals will pop up like they do at Sundance. Despite this, deals are still made, some choose to go into the DIY space and a few (like our release of I Am Divine) succeed in both arenas. The possibilities are endless.
Bryan Glick March 10th, 2014
Posted In: Distribution, Film Festivals, iTunes, Netflix, Theatrical, Uncategorized, Vimeo
Tags: 12 O'Clock Boys, BFI, Bryan Glick, crowdfunding, DIY release, Drinking Buddies, I am Divine, Short Term 12, SXSW, The Film Collaborative, Vimeo
Should you make a horror film?
The month of October seems a good time to look at films in the horror genre and we will be releasing a series of posts all month long that addresses the business of releasing these films.
Long the domain of ultra low budget filmmakers everywhere, horror audiences are now spoiled for choice when it comes to finding a film that terrifies. Yes, everyone with access to a digital camera and buckets of fake blood seems to be honing their craft and turning out product by the thousands. Unfortunately, most of it is high on splatter and low on story and production value. That may have made up the majority of the horror film sales 7 years ago, but distribution advances paid for such films are now exceedingly low (maybe $5K per territory, IF there is a pick up at all) and now the genre is perfect for the torrent sites.Unless you plan to make films as an expensive hobby, the pressure to produce a stellar horror film that people will talk about (see The Conjuring, Insidious, Paranormal Activity) is very high.
The trouble for filmmakers creating in this genre is there is so much being made of questionable quality, it is like asking audiences to find a needle…in a stack of needles (hat tip to Drew Daywalt). The same challenges for fundraising, marketing, and distribution that plague every production, plague horror films as well. To get good word of mouth, the film HAS to be great and have a significant marketing push.
At a recent event hosted at the LA Film School by Screen Craft entitled Horror Filmmaking: The Guts of the Craft, several involved in the horror genre talked about budgeting and distributing indie horror films. All agreed the production value bar has to be raised so much higher than everything else in the market in order to get people to part with their money for a ticket when competing with studio films. Talent manager Andrew Wilson of Zero Gravity Management pointed out that comments like the film did a lot with so little doesn’t hold water with audiences outside of the festival circuit. “You still need it to be good enough to get someone to come into a theater and pay $12…the guy who is going to pay $12 doesn’t care that you did a lot for a little bit of money. They want to see a film that is as good as the big Warner Bros release because they are paying the same amount of money to see it.” While you may be thinking, “I don’t need my film to play in a theater,” and that may be, the films seeing the most revenue in this genre are the ones that do.
The panel also addressed selling horror films into foreign territories. While horror does travel much better than American drama or comedy, there are horror films being made all over the world and some are much more innovative than their American counterparts. France, Japan and Korea were cited as countries producing fantastically creative horror films. American filmmakers with aspirations of distributing their films overseas need to be aware of the competition not just with fellow countrymen, but with foreign talent as well.
Other film distributors are candidly talking about the complete decimation of the market for horror, largely brought on by the internet and piracy, but also a change in consumer habits. Why buy a copy to own of that low grade splatterfest when you can easily stream it (for pay or not) and move on to the next one? More where that came from. There was once big money in fooling audiences to buy a $20 DVD with a good slasher poster and trailer, but now they are wise to the junk vying for their attention and don’t see the need to pay much money for it.
In a talk given last year at the Spooky Empire’s Ultimate Horror Weekend in Orlando, sales agent/distributor Stephen Biro of Unearthed Films actually warned the audience of filmmakers not to get into horror if money was what they were seeking.”The whole system is rigged for the distributors and retailers. You will have to make the movie of a lifetime, something that will stand the test of time.” He confirmed DVD for horror is dead. Titles that might have shipped 10, 000 copies to retailers are now only shipping maybe 2,000. Some stores will only take 40 copies, see how they sell and order more if needed in order to cut down on dealing with returns. Of the big box stores left standing, few are interested in low budget horror titles. Netflix too is stepping away from low budget indie horror on the DVD side. They may offer distributors a 2 year streaming deal for six titles at $24,000 total, but there will be a cost to get them QC’d properly (which comes out of your cut, after the middlemen take their share of course!).
As for iTunes, there are standards barring graphic sex for films in the US and in some countries, they are now requiring a rating from the local ratings authority in order to sell from the iTunes Movie store. The cost of this can run into the thousands (based on run time) per country. Also, subtitling will be required for English language films, another cost.
The major companies in cable VOD (Comcast, Time Warner, Verizon etc) are now requiring a significant theatrical release (about 15 cities) before showing interest in working with a title. They are predominantly interested in titles with significant marketing effort behind them. The cable operators often do not offer advances and you must go through an aggregator like Gravitas Ventures to access. If the aggregator refuses your film, that’s it.
Selling from your own site via DVD or digital through Vimeo or Distrify is still an option, and the cut of revenue is certainly larger. But unless there is a budget and plan in place to market the site, traffic won’t just materialize. Still, for ultra, ultra low budget films (like made for less than $5,000) with a clear marketing strategy and small advertising budget, selling direct is the way to go. Certainly better than giving all rights away for free, for 7 years and seeing nothing. At least your film can access a global audience.
Here is Biro’s talk from Orlando. It runs almost an hour
If after reading this, you are still set to wade into the market with your horror film, stay tuned to future posts looking at the numbers behind some recent horror films and what options you’ll have on the festival circuit.
photo credit: <a href=”http://www.flickr.com/photos/markybon/102406173/”>MarkyBon</a> via <a href=”http://photopin.com”>photopin</a> <a href=”http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/”>cc</a>
Sheri Candler October 3rd, 2013
Posted In: Cable, Digital Distribution, Distribution, International Sales, iTunes, Long Tail & Glut of Content, Marketing, Netflix, Theatrical
Tags: Andrew Wilson, cable VOD, Distrify, Guts of the Craft, horror films, independent film distribution, iTunes, LA Film School, Netflix, Screen Craft, Spooky Empire's Ultimate Horror Weekend, Stephen Biro, Unearthed Films, Vimeo, Warner Bros, Zero Gravity Management
The Audacity of Hope: A Window into the Minds of Filmmakers at Independent Film Week
Next week (September 15 – 19) marks IFP’s annual “Independent FIlm Week” in NYC, herein dozens of fresh-faced and “emerging” filmmakers will once again pitch their shiny new projects in various states of development to jaded Industry executives who believe they’ve seen and heard it all.
Most of you reading this already know that pitching a film in development can be difficult, frustrating work…often because the passion and clarity of your filmmaking vision is often countered by the cloudy cynicism of those who are first hearing about your project. After all, we all know that for every IFP Week success story (and there are many including Benh Zeitlin’s Beasts of the Southern Wild, Courtney Hunt’s Frozen River, Dee Rees’ Pariah, Lauren Greenfield’s The Queen of Versailles, Stacie Passon’s Concussion etc…), there are many, many more films in development that either never get made or never find their way into significant distribution or, god forbid, profit mode.
So what keeps filmmaker’s coming back year after year to events like this? Well, the simple answer is “hope” of course….hope, belief, a passion for storytelling, the conviction that a good story can change the world, and the pure excitement of the possibilities of the unknown.
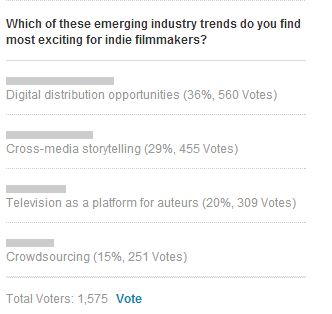
Which is why I found a recent poll hosted on IFP’s Independent Film Week website [right sidebar of the page] so interesting and so telling….in part because the result of the poll runs so counter to my own feelings on the state of independent film distribution.
On its site, IFP asks the following question:
Before you view results so far, answer the question….Which excites YOU the most? Now go vote and see what everyone else said.
** SPOILER ALERT — Do Not Read Forward Until You’ve Actually Voted**
What I find so curious about this is in my role as a independent film distribution educator at The Film Collaborative, I would have voted exactly the other way.
I suspect that a key factor in IFP Filmmakers voting differently than I has something to do with a factor I identified earlier, which I called “the pure excitement of the possibilities of the unknown.” I’m guessing most filmmakers called the thing most “exciting” that they knew the least about. After all 1) “Crowdsourcing” seems familiar to most right now, and therefore almost routine to today’s filmmakers….no matter how amazing the results often are. 2) “Television As a Platform for Auteurs” is also as familiar as clicking on the HBO GO App….even despite the fact that truly independent voices like Lena Dunham have used the platform to become household names. 3) Cross Media Story Telling remains a huge mystery for most filmmakers outside the genre sci-fi and horror realms….especially for independent narrative filmmakers making art house character-driven films. It should be noted that most documentary filmmakers understand it at least a little better. And 4) Digital Distribution Opportunities…of course this is the big one. The Wild West. The place where anything and everything seems possible…even if the evidence proclaiming its success for independents STILL isn’t in, even this many years after we’ve started talking about it.
But still we hope.
From our POV at The Film Collaborative, we see a lot of sales reports of exactly how well our truly independent films are performing on digital platforms….and for the most part I can tell you the results aren’t exactly exciting. Most upsetting is the feeling (and the data to back it) that major digital distribution platforms like Cable VOD, Netflix, iTunes etc are actually increasing the long-tail for STUDIO films, and leaving even less room than before for unknown independents. Yes, of course there are exceptions — for example our TFC member Jonathan Lisecki’s Gayby soared to the top of iTunes during Gay Pride week in June, hitting #1 on iTunes’ indie charts, #3 on their comedy charts, and #5 overall—above such movie-star-studded studio releases as Silver Linings Playbook and Django Unchained. But we all know the saying that the exception can prove the rule.
Yes, more independent film than ever is available on digital platforms, but the marketing conundrums posed by the glut of available content is often making it even harder than ever to get noticed and turn a profit. While Gayby benefited from some clever Pride Week-themed promotions that a major player like iTunes can engineer, this is not easily replicated by individual filmmakers.
For further discussion of the state of independent digital distribution, I queried my colleague Orly Ravid, TFC’s in house guru of the digital distro space. Here’s how she put it:
“I think the word ‘exciting’ is dangerous if filmmakers do not realize that platforms do not sell films, filmmakers / films do.
What *is* exciting is the *access*.
The flip side of that, however, is the decline in inflation of value that happened as a result of middle men competing for films and not knowing for sure how they would perform.
What I mean by that is, what once drove bigger / more deals in the past, is much less present today. I’m leaving theatrical out of this discussion because the point is to compare ‘home entertainment.’
In the past, a distributor would predict what the video stores would buy. Video stores bought, in advance often, based on what they thought would sell and rent well. Sure there were returns but, in general, there was a lot of business done that was based on expectation, not necessarily reality. Money flowed between middle men and distributors and stores etc… and down to the sellers of films. Now, the EXCITING trend is that anyone can distribute one’s film digitally and access a worldwide audience. There are flat fee and low commission services to access key mainstream platforms and also great developing DIY services.
The problem is, that since anyone can do this, so many do it. An abundance of choice and less marketing real estate to compel consumption. Additionally, there is so much less of money changing hands because of anticipation or expectation. Your film either performs on the platforms or on your site or Facebook page, or it does not. Apple does not pay up front. Netflix pays a fee sort of like TV stations do, but only based on solid information regarding demand. And Cable VOD is as marquee-driven and not thriving for the small film as ever.
The increasing need to actually prove your concept is going to put pressure on whomever is willing to take on the marketing. And if no one is, most films under the impact of no marketing will, most likely, make almost no impact. So it’s exciting but deceptive. The developments in digital distribution have given more power to filmmakers not to be at the mercy of gatekeepers. However, even if you can get into key digital stores, you will only reach as many people and make as much money as you have marketed for or authentically connected to.”
Now, don’t we all feel excited? Well maybe that’s not exactly the word….but I would still say “hopeful.”
To further lighten the mood, I’d like to add a word or two about my choice for the emerging trend I find most exciting — and that is crowdsourcing. This term is meant to encompass all activities that include the crowd–crowdfunding, soliciting help from the crowd in regard to time or talent in order to make work, or distributing with the crowd’s help. Primarily, I am going to discuss it in terms of raising money.
Call me old-fashioned, but I still remember the day (like a couple of years ago) when raising the money to make a film or distribute it was by far the hardest part of the equation. If filmmakers work within ultra-realistic budget parameters, crowd-sourcing can and usually does take a huge role in lessening the financial burdens these days. The fact is, with an excellently conceived, planned and executed crowdsourcing campaign, the money is now there for the taking…as long as the filmmaker’s vision is strong enough. No longer is the cloudy cynicism of Industry gatekeepers the key factor in raising money….or even the maximum limit on your credit cards.
I’m not implying that crowdsourcing makes it easy to raise the money….to do it right is a whole job unto itself, and much hard work is involved. But these factors are within a filmmaker’s own control, and by setting realistic goals and working hard towards them, the desired result is achieved with a startling success rate. And it makes the whole money-raising part seem a lot less like gambling than it used to….and you usually don’t have to pay that money back.
To me, that is nothing short of miraculous. And the fact that it is democratic / populist in philosophical nature, and tends to favor films with a strong social message truly thrills me. Less thrilling is the trend towards celebrities crowdsourcing for their pet projects (not going to name names here), but I don’t subscribe to a zero-sum market theory here which will leave the rest of us fighting over the crumbs….so if well-known filmmakers need to use their “brand” to create the films they are most passionate about…I won’t bash them for it.
In fact, there is something about this “brand-oriented” approach to crowdsourcing that may be the MOST instructive “emerging trend” that today’s IFP filmmakers should be paying attention to…as a way to possibly tie digital distribution possibilities directly to the the lessons of crowdsourcing. The problem with digital distribution is the “tree-falls-in-the-forest” phenomenon….i.e. you can put a film on a digital platform, but no-one will know it exists. But crowdsourcing uses the exact opposite principal….it creates FANS of your work who are so moved by your work that they want to give you MONEY.
So, what if you could bring your crowdsourcing community all the way through to digital distribution, where they can be the first audience for your film when it is released? This end-to-end digital solution is really bursting with opportunity…although I’ll admit right here that the work involved is daunting, especially for a filmmaker who just wants to make films.
As a result, a host of new services and platforms are emerging to explore this trend, for example Chill. The idea behind this platform (and others) is promising in that it encourages a “social window” to find and engage your audience before your traditional digital window. Chill can service just the social window, or you can choose also to have them service the traditional digital window. Crowdfunding integration is also built in, which offers you a way to service your obligations to your Kickstarter or Indiegogo backers. They also launched “Insider Access” recently, which helps bridge the window between the end of the Kickstarter campaign and the release.
Perhaps it is not surprising therefore, that in fact, the most intriguing of all would be a way to make all of the “emerging trends” work together to create a new integrated whole. I can’t picture what that looks like just yet…and I guess that is what makes it all part of the “excitement of the possibilities of the unknown.”
Jeffrey Winter will be attending IFP Week as a panelist and participant in the Meet the Decision Makers Artists Services sessions.
Jeffrey Winter September 12th, 2013
Posted In: crowdfunding, Digital Distribution, DIY, Film Festivals, iTunes, Long Tail & Glut of Content, Marketing
Tags: cable VOD, cross media storytelling, crowdfunding, Crowdsourcing, digital film distribution, Gayby, hope, IFP, Independent Film Week, iTunes, Jonathan Lisecki, Netflix, Orly Ravid, The Film Collaborative
Digital distribution AND marketing support is the aim of Devolver
Just prior to SXSW, I was contacted by a new digital distribution outfit called Devolver Digital Film who were launching during the festival. I rolled my eyes as I opened the email because frankly, digital distributors are becoming a dime a dozen and few offer anything that differentiates their services. Yes, they are all non exclusive, but most do not have much to offer in the way of audience recognition of the platform.
Film distribution in some fashion isn’t difficult to obtain anymore…but getting an audience to know a film is available, actively seek it out AND getting them to watch it is another story. So, I was intrigued to find out that Devolver is planning to help solve that problem. Devolver Digital Films is a company expansion out of video game publishing and distribution. Devolver is primarily known for the Serious Sam series of games and their success within the video game industry coupled with founder Mike Wilson’s filmmaking interests lead to a desire to use the same successful game marketing techniques for independent films.
The company’s first title, Cancerpants, is described as “a story about life, love, and a young woman’s journey with breast cancer.” Cancerpants is currently available on VOD networks Verizon and Frontier, and will reach Comcast, Cox, Cablevision, and Dish Online on June 4th. Local theatrical screenings are planned for May 30th in several cities including Grass Valley, CA (hosted by the filmmaker), Los Angeles, Austin, Houston, Oakland, and New York City.
I spoke with Andie Grace, VP of Acquisitions, and Mike Wilson, Partner and filmmaker, to hear what lead to Devolver’s foray into independent film distribution and what they plan to offer that other digital distributors don’t.
AG: “The experience that motivated the creation of Devolver Digital Films comes from the games space. Mike is also a filmmaker and he knows what it is like to run up against the wall of getting distribution. After spending years of making the film, getting your own network together, hitting the festival circuit and landing a distributor and then they put it out, but do little to support it. Devolver Digital would never put out a game that way and now there are so many films on the digital shelves too, a small film that is great could do a lot better with a little help.
When a filmmaker’s own network is exhausted, they themselves are exhausted and ready to move on to another project, they just need a partner to be interested enough to work the title and we saw it as a niche to be filled.”
SC: “Speaking of a niche, does Devolver have a niche audience that they are serving with films? My main problem with film distributors is they don’t really have an audience for their company. They are used to speaking to other businesses (exhibitors, video stores, broadcasters), but not speaking directly to any audience for their titles. Their titles are so diverse that they don’t even really know who is watching. Will this be a unique aspect for Devolver? Is there a Devolver audience?”
AG: “Genre fans definitely stick with a label because of what the label brings them. This is definitely true in the games space. We now have many gamers saying ‘What is my favorite game label going to do with movies?’ So our aim is to keep that fanbase alive and choose films we think they will like.
A lot of counter culture films are coming our way and I definitely look at those films and say ‘I know where to find people who will like this, I know how to organize events around this.”
MW: “Our brand will be built on films that we believe we can make bigger than they would have been without our help. Decisions on films will be based purely on what we think we can do with the network we already have in place. It won’t be according to genr. Inevitably everyone wants us to do films that are considered ‘gamer’ fare. But people who are outside of the gamer world don’t realize that gamers aren’t only into zombie movies or sci fi movies. The independent gamer tends to like lots of independent entertainment. Independent music, independent films, they tend to look a little further past the mainstream. More interesting, less predictable. So that is what we will specialize in.”
SC: “Is there something that the filmmaker has to bring with the project? Do they have to have a certain mentality? Do you want the filmmaker to be an active participant in marketing his/her work, or are you fine with them leaving it with you to make it successful?”
MW: “There are 2 kinds of filmmakers. Those that are exhausted from making the film and just want someone to take care of the rest for them. Some of those are very good films, but there is no promotional hook, and no niche we can tap easily. If they just want it out there, use our service to get it into the world, we’ll put it out for you and you can move on with your life.”
AG: “But we regard this as a partnership. We amplify what they have already started doing on their own. Anyone who wants to just turn tail and walk is probably not going to work well with us. Now, we do understand that by the time the film is ready for distribution, the filmmaker has already exhausted their network and they have done all they know how to do with their Facebook page or Twitter account and they need someone to help them, do it with them. It’s better for them to stay present, be there for the interviews, help craft the story, and use the opportunity to build their own brand as a filmmaker by working with us in a promotional partnership.”
SC: “What will be the range of services Devolver offers? I was thinking it was just digital distribution platforms, but you are working with Tugg to do events too?”
AG: “We will offer cable VOD and internet VOD right now. Being from the games world, we also have our eyes on gaming consoles. We will talk about the total distribution strategy based on the film. It may include using tools like Tugg to do some live event screenings rather than spending time exclusively on the festival circuit. Events can help power the VOD sales. We also will talk about the marketing and publicity, some of the more traditional tactics. We will motivate our own networks to help with promoting screenings. By having the film on VOD when it is in theaters, we can get it highlighted in the ‘in theaters now’ sections of Amazon Instant and such.”
MW: “We are going to be direct to the platforms when that is possible, but until we build up our catalog, it isn’t realistic to think we will be big enough to negotiate direct deals with the bigger players. With our zero overhead, we will be competitive with the percentages we take even when a third party is involved. Plus, we’re going to help promote it which should make the revenue bigger than it would if you went through an aggregator who isn’t doing that.”
SC: “Do you take rights over the film or do those stay with the artist?”
MW: “We wouldn’t take all rights like broadcast network rights, or international rights at the moment. But to the extent that we do put time in to exploit on certain platforms, we want exclusivity on those. It is just bad business for everyone if you have several companies pitching the same film. As a filmmaker, I know there are distributors who want to take all rights just in case in future they want to do something with them. That is not the case with us. Our reason for existence is to avoid that scenario, we have all experienced it as filmmakers ourselves.”
“We do ask for a minimum of one year with options to extend. Most cable operators do want a 5 year minimum. We have found on the games side that there are opportunities for digital bundles and we will want to include our films in bundles without having to keep going back to ask permission. We aren’t going to be releasing 30 movies a month or anything. The films we do have are precious to us and we will be working harder to make the small amount work for us and for the filmmaker.”
SC:”Advertising and promotion aren’t free, they often make up the majority of any kind of film release. Is this a service deal agreement where the filmmaker fronts the money for Devolver to spend or is this more like a traditional distribution situation where Devolver will front the money and recoup from revenue before the filmmaker sees any profit?”
MW: “This won’t be a six figure M&A budget. It is more like soft dollars from us in our organization and network of already existing connections. This is what helps support our games as well. Filmmakers will also be expected to help each other when they are on our label. So anything we provide from this network is just the cost of us doing business and we provide that.”
“Then, if there is an opportunity to buy into a promotional program or whatever, we’ll agree it with the filmmaker and write the check up front and share that cost. If the filmmaker gets a 60% split with us, we share the cost of the promotion.That’s the way we work in games too, it is purely situational. To the extent that they want to be involved, the filmmaker will sign off on any promotion we want to participate in and they will know the whole cost.”
“Another thing we feel is important is being completely transparent. If we do have to go through another distributor to get to a certain outlet, I will forward every royalty statement we get from that distributor so that the filmmaker knows what the revenues were. There has just been too much damage done by ‘Hollywood accounting,’ I use that term to mean all entertainment. The games industry is as bad as any. The little things we can do to remove any doubt about whether we are on the filmmakers team, we will do. The world may not need another VOD distributor, but one thing we will provide that others do not is transparency. There is always room for that.”
SC: “When is the best time for a filmmaker to approach you? In preproduction? Production? Post?”
MW: “I would say in post. We’re not a production company and we aren’t trying to influence the outcome of a movie. We can’t really have a conversation about a film until we know the level of quality it will be. Most of the people we are talking to are in fine cut or have a festival version that they still want to trim.”
AG: “We are having conversations now with people who are in post and it is pretty obvious who their audience is. We are also talking to people who are not going on the festival circuit, they are launching straight into distribution.”
MW: “We have many dream producers coming to us who get this online promotion stuff. We want to network them all together and help to promote each other.”
SC: “How will you bring them together?”
MW: “Google Hangouts I envision. I want just these producers who all have great ideas and are on the same label to get together and brainstorm with each other. Their films are all coming out near the same timeframe so I think some great creativity and excitement will come from it. I don’t think they imagine for a minute that helping someone else will hurt their own projects. It just makes their own network bigger, by aggregating everyone’s together.These are all young, smart, tech savvy producers who want to learn from each other.”
SC: “Well, that is definitely a differentiator for Devolver! Most distributors don’t bother themselves with bring together the filmmakers to help work with all the projects in the catalog. It means you really want to work with filmmakers who are giving, tech savvy and want to help make everyone’s work successful.”
MW: “The filmmaking process just sucks everything out of you, you are totally exhausted when finished and often you are the last man standing. The crew disappears after the wrap party. It will be great to have a company that knows this, pulls together a group of filmmakers in the same situation about to release their films and supports everyone.”
“It is really fun to be coming in at a time when we aren’t having to undo our skills. You go to industry panels where these veteran people are completely unsure of what is happening and frustrated at having to relearn everything because they are used to doing things in a certain way for many years. For us, it is exciting because it is wide open.”
I will be keeping an eye on this young and enthusiastic company. If you have a project you would like to approach Devolver Digital Films about, contact Andie Grace:
films [at] devolverdigital dot com
Sheri Candler May 9th, 2013
Posted In: Amazon VOD & CreateSpace, Digital Distribution, Distribution, iTunes, Netflix
Tags: Andie Grace, Cancerpants, Devolver Digital Films, Digital Distribution, digital distributor, independent film, Mike Wilson, Serious Sam, Tugg
Indie Game: a distribution case study
This article first appeared on the Sundance Artist Services blog on August 13, 2012
written by Bryan Glick with assistance from Sheri Candler and Orly Ravid
Indie Game: The Movie has quickly developed a name not just as a must-see documentary but also as a film pioneer in the world of distribution. Recently, I had a Skype chat with Co-directors James Swirsky and Lisanne Pajot . The documentary darlings talked about their indie film and its truly indie journey to audiences.
 Swirsky and Pajot did corporate commercial work together for five years and that eventually blossomed into doing their first feature. “We thought it would take one year, but it ended up taking two. I can’t imagine working another way, we have a wonderful overlapping and complimentary skill set, ” said Pajot. “We both edited this film, we both shot this film. It creates this really fluid organic way of working. It’s kind of the result of 5 or 6 years of working together. I don’t think you could get a two person team doing an independent film working like we did on day one. It’s stressful at times but the benefits are absolutely fantastic, ” said Swirsky.
Swirsky and Pajot did corporate commercial work together for five years and that eventually blossomed into doing their first feature. “We thought it would take one year, but it ended up taking two. I can’t imagine working another way, we have a wonderful overlapping and complimentary skill set, ” said Pajot. “We both edited this film, we both shot this film. It creates this really fluid organic way of working. It’s kind of the result of 5 or 6 years of working together. I don’t think you could get a two person team doing an independent film working like we did on day one. It’s stressful at times but the benefits are absolutely fantastic, ” said Swirsky.
According to Swirsky, Kickstarter covered 40% of the budget. “We used it to ‘kickstart’, we asked for $15000 on our first campaign which we knew would not make the film, but it really got things going. The rest of the budget was us, personal savings.” The team used Kickstarter twice; the first in 2010 asking for $15,000 and ended up with $23,341 with 297 backers. On the second campaign in 2011, they asked for $35,000 and raised $71,335 with 1,559 backers.
The hard work, dedication, and talent paid off. Indie Game: The Movie was selected to premiere in the World Documentary Competition section at the 2012 Sundance Film Festival winning Pajot and Swirsky the World Cinema Documentary Film Editing Award . “[Sundance] speaks to the independent spirit. It’s kind of the best fit, the dream fit for the film. Just being a filmmaker you want to premiere your film at Sundance. That’s where you hear about your heroes,” noted Swirsky. “Never before in our entire careers have we felt so incredibly supported…They know how to treat you right and not just logistics, it’s more ‘we want to help you with this project and help you next time.’ It was overwhelming because we’ve never had that. We’ve just never been exposed that,” interjected Pajot
They hired a sales agent upon their acceptance into Sundance and the film generated tons of buzz before it arrived at the festival resulting in a sales frenzy. The filmmakers wanted a simultaneous worldwide digital release, but theatrical distributors weren’t willing to give up digital rights so they opted for a self release. “There were a lot of offers, they approached us to purchase various rights. We felt we needed to get it out fairly quickly and in the digital way. A lot of the deals we turned down were in a little more of the traditional route. None of them ended up being a great fit,” said Pajot.
Several people were stunned when this indie doc about indie videogame developers opted to sell their film for remake rights to Scott Rudin and HBO. Pajot explained, “He saw the trailer and reached out a week or so before Sundance. That was sort of out of left field because it wasn’t something we were pursuing.” Swirsky added, “They optioned to potentially turn the concept into a TV show about game development…As a person who watches stuff on TV, I want this to exist. I want to see what these guys do with it.” The deal still left the door open for a more typical theatrical release. However that was only the start of their plan.
“We had spoken to Gary Hustwit (Helvetica). We sort of have an understanding of how he organized his own tours. We had to make our decision whether that was something we wanted to utilize. Five days after Sundance, we decided we would and were on the road 2 weeks after… Before Sundance this was how we envisioned rolling out…[We looked at] Kevin Smith and Louis C.K. and what they’re doing. We are not those guys and we don’t have that audience, but knowing core audience is out there, doing this made sense,” said Swirsky.
They proceeded to go on a multi-city promotional tour starting with seven dates and so far they have had 15 special events screenings of which 13 were sold out! This is separate from 37 theaters across Canada doing a one night only event. They also settled on a small theatrical release in NYC and LA. When talking about the theaters and booking, they said theaters saw the sellout screenings and that prompted interest despite the fact that the film was in digital release. They accomplish all of this with a thrifty mindset. “P&A was not a budgetary item we put aside and if an investment was required, we would dip into pre orders. We didn’t put aside a marketing budget for it,” said Swirsky. Regarding the pre order revenue, they sold a cool $150,000 in DVD pre-orders in the lead up to release of the film. From this money, they funded their theatrical tour.
While the theatrical release was small, it generated solid enough numbers to get held over in multiple cities and provided for vital word of mouth that will ultimately make the film profitable. The grosses were only reported for their opening weekend, but they continued to pack the houses in later weeks.”I don’t look back at the box office. The tour was more profitable than the theatrical…They both have the benefits, having theatrical it gets a broader audience. It was more a commercial thing than box office,” said Swirsky. “We are still getting inquiries from theaters. They still want to book it despite the fact it’s out there digitally,” said Pajot. “We had this sort of hype machine happening. We didn’t put out advertising. Everything was through our mailing that started with the 300 on our first Kickstarter and through Twitter,” said Swirsky. Now the team has over 20,000 people on their mailing list and over 10,000 Twitter followers. In order to keep this word of mouth and enthusiasm going, the filmmakers released 88 minutes of exclusive content – most of which didn’t make the final cut – to their funders, took creative suggestions from their online forum and sent out updates on the games the subjects of their film were developing over the course of the two years the film was in production.
Following the success the film has enjoyed in various settings, Indie Game: The Movie premiered on three different digital distribution platforms. If you were to try and guess what they were though, you would most likely only get one right. While, it is available on the standard iTunes, the other two means of access are much more experimental and particularly appropriate for this doc.
It is only the second film to be distributed by VHX as a direct DRM-free download courtesy of their, ‘VHX For Artists‘ platform. Finally, this film is reaching gamers directly through Steam which is a video game distribution platform run by Valve. This sterling doc is also only the second film to be sold through the video game service, where it was able to be pre-ordered for $8.99 as opposed to the $9.99 it costs across all platforms. This is perhaps the perfect example of the changing landscape of independent film distribution. Every film has a potential niche and most of these can arguably be reached more effectively through means outside the standard distribution model. Why should a fan of couponing have to go through hundreds of films on Netflix before even finding out a documentary about couponing exists, when it could be promoted on a couponing website?
As they are going into uncharted territory, both Pajot and Swirsky avoided making any bold predictions.”It’s just wait and see. It’s an experiment because we’re the first movie on Steam. We’re really interested to look at and talk about in the future. I don’t want to make predictions…I do think documentary lends itself to that kind of marketing though. We’re trying to not just be niche but there is power in that core audience. They are very easy to find online,” said Swirsky.
Just because they are pursuing a bold strategy doesn’t mean they were any less cost conscious. “The VHX stuff, it was a collaboration, so there were no huge costs. Basically subtitles, a little publicity costs from Von Murphy PR and Strategy PR who helped us with theatrical. Those guys made sense to bring on,” said Pajot. “A lot of our costs were taken up by volunteers. If they help us do subtitles, they can have a ticket event, a screening in their country,” added Swirsky.
They also note that a large amount of their profit has been in pre-orders. 10,000 people have pre-ordered one of their three DVD options priced at $9.99, $24.99 and a special edition DVD for $69.99 tied with digital. While the film focused on a select few indie game developers, they interviewed 20 different developers and the additional footage is part of the Special Edition DVD/Blu-Ray. That might explain why it’s their highest seller.
All this doesn’t mean that any of the dozens of other options are no longer usable. Quite the contrary, they have also taken advantage of the Sundance Artist Services affiliations to go on a number of more traditional digital sites. Increased views of a film even if on non traditional platforms can mean increased web searches and awareness and could be used to drive up sales on mainstay platforms.
The real winner though is ultimately the audience. For the majority of the world that doesn’t go to Sundance or Cannes each year, this is how they can discover small films that were made with them in mind. The HBO deal aside, this is bound to be one incredibly profitable documentary that introduces a whole new crowd to quality art-house cinema. “We are still booking community screenings. If people want to book, they can contact us…We are thinking maybe we might do another shorter tour at some point,” said Pajot.
Here’s to the independent film spirit, alive and well.
Update Feb 2013: The creators of Indie Game have written their own case study discussing the many tools and techniques they used. Head over to their website for the full study.
Orly Ravid August 16th, 2012
Posted In: Digital Distribution, Distribution, DIY, Film Festivals, iTunes, Marketing, Publicity, Theatrical
Tags: crowdfunding, DIY distribution, documentary, game developers, Gary Hustwit, independent film, Indie Game, James Swirsky, Kevin Smith, Kickstarter, Lisanne Pajot, Louis C.K., self distribution, Steam, Sundance Artists Services, Sundance Film Festival, VHX, VHX for Artists
Lead up to Cannes: Digital Distribution Beyond the Old World
This post was originally published on the Sundance Artists Services blog on April 23, 2012. This is an interview between Rights Stuff’s Wendy Bernfeld and The Film Collaborative’s Orly Ravid on the state of digital in Europe
In the past, many new media and VOD platforms – whether based on pay-per-transaction (TVOD), subscription (SVOD), free to user/ad supported (ADVOD) or download to own (DTO) — came and went, to the disillusionment of those brave souls trying to explore and develop the new sector and audiences.
Some filmmakers, sales agents, distributors who dared to license were wonderfully pleased with surprisingly good results for particular films (and not always the same ones that were mainstream successes in traditional media), but on balance, let’s face it, most were underwhelmed with the lackluster performance or transience of the various sites, and eventually became jaded about the whole sector. But it’s no longer a viable option just to sit back.
Over the past 18 months particularly the digital/VOD sector (including internationally) has finally begun paying off well for filmmakers, producers, distributors, and sales agents… at least for those who are willing to take the time to navigate (alone or partnered with others) the complexities of the sector, play with creative ”windowing’’ while balancing opportunities from traditional media, and accept initially more modest revenues from multiple smaller deals across various platforms and regions (yielding cumulative revenues in a largely non exclusive sector).
In addition to traditional media deals and VOD deal potential with IPTV, telecom, and cable offerings, and larger American sites (e.g. Hulu, YouTube, Netflix, iTunes), your film may well find interested audiences and homes on EU/international platforms…even if not picked up in the USA.
HOW IS INTERNATIONAL DIGITAL DIFFERENT FROM THAT IN THE USA?
The EU (beyond UK) deals with multiple languages, different tastes and appetites, different windows (vs consistent release patterns/dates per country), different platforms to navigate and balance against multiple different traditional media buyers, and, to be honest in general more work for smaller potential revenues from each deal/window.
But on the plus side, films can find homes overseas in many markets and windows, even if not ending up in the mainstream or major US/UK platforms.
The UK is at the moment probably the more stable and lucrative for English (the VOD market is already very competitive, with large platforms like Netflix, Lovefilm, BSkyB, FilmFlex, iTunes, and Blinkbox) but as soon as you ripple out to EU, digital distribution will take more work and art and generate relatively less money, especially if your film is only in original English language, and not already exposed in terms of promo/PR (theatrical, DVD release in the region etc.). However, there is indeed a growing appetite by now for art house, festival, docs, quality indie films, and foreign language films, if well curated, e.g. around festivals/brands/themes rather than as one-offs.
WHO’S OUT THERE in EU and what are some of the key territories where digital is meaningful?
Digital is immediately more meaningful in the UK, France, the Nordic region, and in Benelux, where there are already pc/mobile and tech-savvy customers and a willingness to view films in English with subtitles (vs. the dubbed regions of Germany, Spain, Italy etc., where one has to invest more to get the languages to cross over).
Although publications often refer to figures noting several hundreds of VOD platforms in Europe, in my view there are only probably 100 or so that are worth talking about when discussing licensing—half of which the main revenue generators, and another half of which are still potentially significant buyers(depending on the film of course)
In Europe, as in America, transactional VOD (pay per view) platforms are more established – some regional (per country), and others multi region (e.g. Acetrax, UPC/Chello, Headweb, iTunes, Playstation Network Live, Voddler, Xbox Live). Outside of the UK, one obviously enhances possibilities if addressing customers in their own languages and tailoring content to local preferences such film classification, advertising, and general consumer and cultural tastes.
iTunes has only recently (in autumn 2011) begun to expand its footprint into Europe, including in the following EU countries: Austria, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Greece, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Republic of Ireland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. Non-English stores include: Spain, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, Belgium, Switzerland, and Portugal. They also just recently launched in Brazil / Latin America as well.
NETFLIX, Amazon (via Lovefilm), and Hulu are expanding their international footprint too. Netflix, for example, recently launched in UK/Eire, and is anticipated to roll into other regions such as Spain thereafter, and has already extended its occasionally original production commissioning activities to EU (e.g. Denmark – Lillyhammer deal, and more recently France (Gaumont etc) – Hemlock Grove series funding ). Lovefilm already has a presence beyond the UK (in Germany and Nordic), and is anticipated to expand regions. Hulu has not yet launched in EU but did launch already in Japan. As part of its competition rampup (in the US against Netflix in the SVOD market, it has also began commissioning original programming, (Day in the Life – Morgan Spurlock, for example, which was just picked up by Fremantle for distribution thereafter)….and also continues seeking special films or shows to do stunts around. We understand that they are trying to acquire more Spanish rights for the US…an important strategic move for other US players trying to expand their footprint in EU as well. Meanwhile in early 2012 the UK became a hotbed of activity for SVOD, with deals that would formerly have been nonexclusive (with e.g. Netflix, Lovefilm) being now struck on a lucrative exclusive basis, following the example of the competitive SVOD vs. Pay TV market in the US.
So what are the other key EU platforms? Trends?
Various international platforms are now becoming increasingly interested in licensing more art house, niche and festival films–not just mainstream titles. It is expected that some of the larger brand sites this year (e.g. those in UK like Netflix, Lovefilm, etc.) will expand the indie/art house and festival category further, and also be open to foreign language films (dubbed or subtitled as applicable per country audience as above). Most deals for art house/fest films, where not locally versioned or released in theatres or DVD, are on a non exclusive rev share basis, and in some cases where there is particular acclaim or cast, it can be coupled with a modest upfront, while if on an SVOD basis, flat fee deals apply (similar to non-exclusive Pay TV licensing deal parameters).
But in countries where the Pay TV incumbent is competing against a new web player, such as a traditional Pay TV player “vs.” SVOD (like Netflix “vs.” HBO in the US, or Lovefilm/Amazon “vs.” BSkyB in UK), as above, the fees can be more lucrative, in the form of true flat license fees in the Pay TV range. – whether on exclusive or non exclusive basis, and thus matching or exceeding the normal price ranges before the competition. As well, when competition heats up over one category of title, it’s also not unusual to have the competitors round out, extend, or diversify their consumer offer and move into other genres, to try to distinguish themselves from the competition. This is happening in more and more countries– for example the Netherlands, where HBO /Ziggo just launched in February and the local incumbent, Film1, responded by adding a branded art house/indie thematic channel (Sundance Channel).
Key note: Deals are generally non-exclusive and thus if carefully staggered, one can license the film sequentially through various windows (TVOD, SVOD, AVOD, and if applicable, DTO) and in multiple regions.
An example: one can first license a current film for transactional VOD (TVOD) on a rev share basis to cable and telecom VOD platforms (like France Telecom/Orange, UPC, etc) as well as (simultaneously) web based players (e.g. iTunes), then to subscription -based windows (premium Pay TV (e.g. HBO, Viasat) and their corresponding “TV Everywhere” offerings, thematic Pay TV, and/or standalone SVOD services . Thereafter, the film can move to other ad-supported services (free to consumer, web based, e.g. YouTube AVOD). This pattern can apply in multiple countries.
As mentioned above, there are hundreds of local European platforms —both standalone web-based services and mainstream and/or local telecom and Cable VOD platforms that have online offerings of their own. VIASAT, for example, was historically a premium pay service, but now offers not only conventional Pay TV and ”TV Everywhere” but also standalone thematic offerings to non-subscribers (SVOD to PC). Similarly, BSkyB just announced the upcoming launch of NOW TV – also aimed at non- subscribers (“Cord Nevers, and/or Cord Cutters”) – a thematic SVOD/low pay offering of films.
Opportunities will only increase in 2012 and 2013 as more from USA players, sites, and OTT box offerings beyond Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon gradually cross over to EU/international markets particularly if the new services don’t limit themselves to mainstream offerings and tastes.
Getting to the platform: As in the United States, some of the larger platforms (such as LOVEFILM, BlinkBox, Netflix, itunes) only take larger packages of films with a minimum volume, and are unwilling to deal direct with producers and distributors for “one off” deals. Until recently, most of the larger sites also focused mainly on mainstream films. In general, these services steer filmmakers towards conventional distributors, or aggregators/digital distributors like Movie Partnership (UK); but sometimes will accept dealings direct for certain films, or will go via an agent working on a flat fee basis (like Rights Stuff / Film Collaborative). In the latter scenario, the film IP remains in the filmmaker’s/distributor’s name, the money from deals flows to them directly and they get access and paid advice through third party consultants/agents/advisors.
Up until now, having had a DVD and/or local theatrical release was quite important for enhancing deals. But increasingly now online sites are willing to handle more innovative windows, e.g. premiering films online, or Day & Date with other windows (or shortly thereafter). Lesser-known or library (catalog) films can usually find a home on a non- exclusive and on ad-supported (AVOD) basis, but more current films usually start with transactional (TVOD) basis and/or subscription platforms (SVOD)… If filmmakers have titles already encoded to the expensive iTunes spec, this can be helpful in wider distribution, but it’s not essential; many digital platforms are now willing to take delivery of indie or art house films even via DVD or a hard drive/ digital master.
In terms of deal models, some aggregators (middlemen) take larger %s but then take care of all encoding and delivery fulfillment, while others who are more in an advisory or agent role take a lower share for deal making and platform access but leave you to arrange the encoding separately. In some countries (e.g. Brazil), platforms may not take English versions unless local subtitles or dubs are available, and work with distributors who create versions where necessary. These distributors co-curate packages with filmmakers based on experience of what “moves” best in the region so as not to invest in encoding or language versioning for films that may not generate enough revenue to justify it…
A side note regarding subtitling, by the way: Film Collaborative is looking into software that helps facilitate dubbing in the same voice as the actor/speaker, but meanwhile in any case, subtitling for digital is getting less and less expensive and can be done via relatively inexpensive software or labs. If one has shown a film at a film festival in another country and plans to then distribute the film there, we’d recommend you ask the fest for access to the subtitles (if cleared for other distribution). Traditionally, Nordic, Benelux, and some other regions are fine with and prefer subtitles, while others (such as Germany, Spain, and Italy) require dubbing. However, in the higher-educated arthouse/filmfest world, one can often get away with just subtitled versions even in the dubbing countries.
As indicated above, for better platform access, one may want to pick or join with new media /digital distribution specialists – particularly if your traditional sales agent or distributor, strong in conventional media (theatrical, video etc.) is however not active or savvy in the VOD landscape above (platforms, deal terms, contacts etc). Otherwise it can be a self-fulfilling prophecy that you then ”don’t make money in digital’’. It’s a balancing act of cost vs. services, and a lot of work in international!
And filmmakers, whatever you choose to do with respect to your digital distribution, do not forget that one can also reach the whole wide world via one’s own website(s) and social networking pages by utilizing DIY digital distribution services (for more on this topic please refer to numerous past blog posts about digital distribution and DIY platforms and services at www.TheFilmCollaborative.org/blog and/or the Resource Place at www.TheFilmCollaborative.org/ResourcePlace).
As for piracy: in various cases filmmakers can tap into or derive indirect benefit from these online communities. See for e.g. Sheri Candler’s case studies in www.SellingYourFilm.com, Some filmmakers partner with Bit Torrent, Pirate Bay etc to launch their films online, tapping into the audiences already there (e.g. Nasty Old People, The Tunnel, Yes Men Fix the World).
LET’S TALK ABOUT POTENTIAL FUTURE TRENDS:
Diversification, Cross Platform/Transmedia: We believe 2012 will see continued consolidation of platforms and fuller diversification within the genres offered. Also as above, some key platforms (such as Hulu, Netflix, Yahoo, Endemol/AOL, Nokia, Canal+, Orange, ARTE, Channel4, ) are now also selectively commissioning transmedia and/or branded film opportunities (YouTube has not begun funding outside US yet). New funds and educational bodies (including MEDIA, Power to the Pixel) are increasing the emphasis on digital as a 360 proposition from inception of the film production process.
Multi-Layered Business Models: Platforms’ business models are also starting to become more multi-layered to handle different genres, consumer price points, and windows. For example, AVOD platforms such as YOUTUBE and SVOD platforms such as Lovefilm are now adding premium transactional VOD (TVOD) in order to handle current films. And as above, SVOD players are expanding their offerings beyond just library titles, beginning to buy newer and newer films in order to compete against premium PAY TV. This trend is continuing in the newer launching countries, e.g. Holland and Brazil where new PAY TV and localized SVOD and AVOD entrants have launched (e.g. YouTube regional sites). YouTube is also commissioning Made for Web content (MFW), although first in English language countries.
Festivals: Some European festivals have also recently started offering select titles on a TVOD basis. Rights Stuff recently worked with IDFA.tv to put around 100 films online—some on an AVOD basis and some on a TVOD basis—and in future more will follow. Certain other festivals (such as IFFR) have also begun to follow the US festival path of offering limited TVOD around or during the festival. This can open many doors for filmmakers, but also requires careful juggling and balancing when figuring out distribution patterns for conventional vs. online and new media….the balancing act is always key.
Traditional Players add VOD as well: As to the more traditional PAY TV players, last year after EPIX began licensing international festival documentaries it then turned its focus more to co-productions instead of acquisitions. And over 2011/12,As in the US, many traditional PAY TV platforms are going cross-platform and on multiple devices (a la “TV EVERYWHERE”, and similarly the nonlinear online channels are often seeking multiple device rights and/or at least have an App). Thus balancing traditional PAY TV sale vs. digital media requires more attention in rights grants and windows, but offers more opportunity correspondingly. In terms of trends, it still seems like the bigger funds and platforms are still more focused on more mainstream content, however as above this is starting to expand in EU to a wider net of content and genres.
REGIONAL EXAMPLES: VOD LICENSING PLAYERS AND WINDOWS in EU:
For bigger indie titles and mainstream ones, there are usually about 5-8 or so VOD outlets that one can target per country. Most of these will buy TVOD rights and sometimes also SVOD and/or AVOD. Platforms include television-related services (IPTV, Telecom/Cable companies, etc), as well as online and/or mobile sites, OTT box offerings, and consumer electronic (e.g. connected TV) portals.
For e.g. in Holland, a film or TV show can have various TVOD deals, not only with MSO like KPN, Tele2, Ziggo, and UPC, but also with web based services like Cinemalink.nl (for art house), iTunes, and the newly launched service from theatrical distributor Pathé (a Rights Stuff client), pathethuis.nl a bold move by a traditional theatrical exhibitor to also launch and embrace TVOD for a fuller offer to its film-loving audience base.
That would then be then followed by Premium PAY TV and/or SVOD sales (e.g. Film1, Ziggo/HBO, Ximon, Mubi.com), then AVOD (YouTube, IDFA.tv) with various competing players per region. The same film can also attract interest of foreign platforms not yet launched in the region but scaling up behind scenes, poised to launch there (e.g. those seeking to next move after UK into, say, Spain or other Benelux regions/Nordic). And this is on top of the broadcaster based proprietary VOD services (e.g. RTLXL and Veamer (from SBS and public TV catchup sites.
There are also various local equivalents of genre sits like Fandor or IndieFlix in certain EU regions. MUBI (www.Mubi.com) (co-owned by the rights holder to one of the most expansive libraries of art house cinema, Celluloid Dreams) is technically available everywhere, and is sometimes syndicated as an SVOD channel to telecom platforms (as in the case with Belgacom in Belgium). It is also on Sony Playstation. Last we checked, 60% of its audience was the US and most of the rest in Europe. Revenues from it for our films (TFC) have been small to-date, low 3-figures but it’s a good pedigree platform and perhaps revenues will increase.
A few others in EU include e.g. Orange, Canal Plus, (France and, multi region), Telenet, Belgacom, (in Belgium), SF Anytime, Voddler Film2home, Headweb , Viasat etc in Nordic /other regions), Telefonica, … Maxdome (Germany), Sony-related Qriocity, Daily Motion (many countries in EU), Movieeurope, Zattoo. Sales agent Wild Bunch has also recently launched a platform service called FilmoTV.
And as an aside, in Brazil/Latin America, the market has been heating up intensely in late 2011/12, with various TVOD and IPTV platform launches players, as well as competitive new PAY TV and SVOD services (eg Netflix, Netmovies, Terra) springing up or extending VOD. NewPAY TV laws (from fall 2011) are resulting in more potential competition, which is good news for filmmakers seeking new audiences over there. Our recommended approach to filmmakers seeking deals in this region is to partner locally, e.g. with ELO Distribution, with whom we work traditional and non-traditional (new media) players.
These are just a few categorical examples…there are plenty more buyers and platforms emerging internationally, including consumer electronics manufacturers (such as Samsung and tablet and connected TV manufacturers in EU and internationally who are getting into the game either on the licensing front or occasionally even funding/commissioning Transmedia or mfw (Made for Web). However, these usually license fuller sites (like a Lovefilm or Snagfilms) and not individual one –off titles.
Overall, there are a lot of small markets and platforms, and all this takes a lot of work, but if one has built community around a film and awareness then the effort may pay off and add up to a nice revenue stream. Once the first deals are in place with platforms (deal structures, relationships, contacts, contracts) it’s easier to build on that and add new films to the deals with just short amendments or riders, so the effort at the front end makes years of future dealings run smoother.
TRENDS RE: OTHER GENRES:
Aside from art house, festival indie films, and docs, one area that we expect to see more SVOD licensing around is kids’ films. Various smaller sites also have a strong appetite for gay/lesbian, martial arts, and horror programming, graphic novels, and made for web/cross platform/Transmedia original productions…but one has to be selective. As to documentaries, the combination of a large number of doc sites in the EU with the heavy exposure of docs on public and conventional TV in EU means docs can be relatively harder to monetize here, unless well curated and packaged, for e.g. under a larger brand/festival, like IDFA.
WINDOWING:
Typically films follow the sequential windowing described above when moving through the Transactional, Sell Through, Subscription, and ADVOD windows. But for certain films it it can be clever and compelling to have windows intentionally reversed or out of sequence. For example, premiering a film ONLINE or day-and-date with another cross-promoted window ahead of theatrical, and heavily emphasizing social media marketing can allow producers to build (and engage with) the audience before the film is even out. The key is to know your audience and try to tailor the marketing and distribution patterns accordingly…producers can be more active these days to heighten the chances of film success.
More and more platforms are open to this REVERSE WINDOWING (which began successfully in the US, e.g. with Lars von Trier’s Melancholia), . For example, in Holland, the film Claustrophobia launched online first and its success via social networking ultimately brought it a theatrical deal. In another case, Submarine NL’s film ‘’Molotov Alva’’ (a second life documentary released online virally first) later secured a HBO sale on premium pay tv, and in another film we worked with (the documentary Surfing and Sharks), intensive social network/audience engagement before and during the film’s festival exhibitions helped not only to enhance the potential audience for the film ahead of commercial released, but also to attract wider sponsor support. Ultimately, the visible online appetite for the film (including the number of Twitter and Facebook followers amassed in a very short time) helped result in a stronger all-rights distribution deal as well.
There are various new platforms focused on these models that are launching and expanding reach in EU– e.g. EU1 (The Makers Channel), which just launched in the Netherlands and will soon expand to other EU regions. One part of the site is business-to-business (geared towards talent, directors, actors, producers, etc.) providing for online pitches and related crowd sourcing and crowd funding (like Kickstarter). The other component is business to consumer, and allows exhibition of works online, on a rev share VOD basis… which will be coupled for the first time with TVOD exhibitions on UPC/Chello/Ziggo (the Cable TV VOD platform partners) thus giving much wider audience reach than conventional web VOD to PC. In some cases films can also combine a theatrical (conventional or event theatrical local) release for the films “day and date” with or in staggered creative windows. We are working with two English film cases in NL already, and as this site expands to other regions and to wider English crossover, this will open up many more opportunities (in some ways similar to what you see already in the USA on Tribeca/Sundance with exhibitions on cable households (TVOD).
SHOW ME THE MONEY:
Even where indie features have no theatrical or DVD release, if there is some cast and acclaim from festivals, and the film is new/current, TVOD is possible . This is usually on a rev share basis (with %s ranging from 50-50 to 70-30, with various deductions to negotiate). In SVOD/PAY TV, flat fees are normally paid instead of rev share, usually, along lines of comparable non-exclusive PAY TV license fees for indies. For example, in medium sized, non-English language EU countries, we’ve seen SVOD flat fee prices range from 5K-50K per title where it’s been theatrically or DVD released, etc, while with less exposure or more niche, sometimes the flat fees can be lower and more aligned with AVOD. In AVOD, deals are usually rev-share, (50-50 to 70-30) with sometimes a small upfront fee. In a medium-sized EU region, MG’s (Minimum Guarantees), when given at all for indie film, can range from a few hundred dollars (plus rev share) to 1-2K for higher end material. The very largest platforms may get away with no upfront fees at all due to their scale and reach, but smaller EU sites may well, depending on the film, offer something modest. When you do multiple nonexclusive deals, these can add up and help defray some costs of versioning, digitization, deliveries, etc.
As to revenues generated from VOD once the license is done: again it is platform and film specific, and one cannot generalize. We’ve seen certain cases where niche foreign language art house films yielded 40K in 2 months of non-exclusive TVOD revenues across a few platforms, , while other titles from the same distributor yielded only 1-2K in the same deals/time period. Things are similar with SVOD – fees can range in one small non-English EU country from 5k to 40k for a single SVOD window license fee (non exclusive) – so the key is still in our view still to engage in a reasonable number of deals in each country across various windows, platforms and business models.
IN SUM: SOME TIPS FOR GOOD RESULTS IN DIGITAL DISTRIBUTION:
- We strongly advise building audience for the film before release, even while the film is still being made. Engage in social media marketing around the themes of your film and the cast: Twitter, Facebook, YouTube (promos) etc. This not only enhances the audience and reach of your film, when it is released, but potentially your distribution and/or digital deal making as well.
- Once a deal is done and even after the film is sold, it still helps for the producer or distributor to take an active role in social media marketing, e.g. to direct attention (via social media etc.) to scheduled exhibitions of the films on various platforms licensed. Many platforms in EU are still showing viewers EPG’s with clumsy alphabetical “listings’’(as opposed to the type of creative Netflix/Lovefilm recommendation engines and suggestions), so helping viewers find the film will in turn increase returns.
- As for digital deals: We’d also recommend that individual producers who cannot afford tailored individual advice consider combining forces via producer groups to collectively fund some serious upfront advice – help each other curate more attractive packages of their better material, so easier to sell on to platforms directly or indirectly – and grouped in many different ways (theme, genre, category, audience etc.).
- If necessary, try to have “split rights’’ deals. If the person to whom you are entrusting the film in an “all rights” deal is less strong in digital and likely to “sit on” new media rights, you can explore splitting these rights /sharing them non exclusively with the distributor and another specialized digital distributor, case by case. Rights Stuff has often done this working with sales agents and distributors and producers directly to maximize digital distribution.
- Work with festivals (both traditional and online), who can play an increasing role in EU as they cross over to the digital space and VOD offerings. But be careful about the scope and duration of rights granted vs. other traditional and digital media, to maximize potential in all areas.
- Don’t abdicate completely, ie don’t’wash your hands of the film once you put it in someone else’s hands (the conventional sales approach) – keep involved along the way, gain as much learning as possible, split revenues, resources, knowledge base, contacts … and lever the outcomes to your next and future films.
Final notes: Pricing of films on the transactional side is relatively commensurate with that in the US, however non USA SVOD and AVOD markets are smaller with lower revenue per deal. . We did not include VIEWSTER in this article but feel free to check them out. They are a consumer-facing platform that also supplies other platforms (i.e. functions like an aggregator). They seem to favor films with cast, more commercial films and those with a bigger profile. www.Viewster.com
Orly Ravid May 15th, 2012
Posted In: Digital Distribution, Distribution, Distribution Platforms, Hulu, International Sales, iTunes, Netflix
Tags: aggregators, AVOD, digital distribution in Europe, distributor, DTO, independent film, Orly Ravid, release windows, Rights Stuff, sales agent, subtitling, Sundance Artists Services, SVOD, The Film Collaborative, TVOD, Viewster, Wendy Bernfeld
Subtitles in Digital America
Recently I was invited to be on a panel at the International Film Festival Rotterdam (IFFR) and participate in their mentoring sessions and the lab at Cinemart. Great experience. I am always amazed by the difference between the US and Europe. The whole government funding of films and new media initiatives as our government is about to shut down. Well, their policies and practices do take their own financial toll too but one I think is worth it. For all my europhileness I have to note that the Europeans can be just as guilty of not wanting to watch subtitles in fact some countries dub films instead. And of course we know that Hollywood is big business in Europe too. But all in all, art house cinema seems to reach more broadly in Europe and even some parts of Asia than it does in the US. Films in Cannes and other top fests can sell all over Europe and never in the US or success in opening theatrically only in NY and maybe LA and overall it seems to me box office is generally down for foreign language cinema.
International filmmakers want US distribution and it was painful for me to discuss their prospects at IFFR because for so many, the prospects are slim. But this one’s for you! (Please note this blog is focused on digital distribution and not healthy categories for foreign language cinema such as Non Theatrical including Museums, Films Festival, Colleges, Educational / Institutional).
Cable VOD was 80% of the digital revenue in the US in 2009 but it’s now declining little by little, now estimated to be in the high 70’s (approx 77%) and may decline further still. The reason for this change, which is expected to continue, is that Internet based platforms are growing. Regarding FOREIGN LANGUAGE ON CABLE VOD: Distributors and aggregators agree that foreign language cinema is very hard to get onto Cable VOD platforms and slots for non-English cinema are reserved generally for marquee driven films and/or films with a real hook (name cast/director, highly acclaimed, genre hook). A big independent Cable VOD aggregator notes a real struggle in getting foreign language films to perform on Cable VOD and even Bollywood titles that had wide theatrical distribution and a box office of upwards of $1,000,000 still perform poorly (poorly means 4-figure revenue, 5-figure tops). They have had some success with foreign martial arts films and will continue with those in the foreseeable future. Time Warner Cable (TWC) remains more open to foreign language cinema though it plays the fewest films, a range between 190 – 246 at any given time (with a shelf life usually of 60 days and with 2/3rd of the content seeming to be bigger studio product, and the rest indie). By comparison Charter and AT&T play about 1,000 and Verizon plays 2,000, and Comcast plays about 4,000. [See below for the 2010 breakdown of Cable subscription numbers.] Hence, individual titles may perform better on Time Warner Cable for obvious reasons, Comcast may have more subscribers but there’s less competition and TWC is in New York, the best demographic for art house cinema.
Generally speaking, platforms overall are far more receptive to foreign films following the recent success of DRAGON TATTOO, TELL NO ONE, IP MAN, etc. than they have ever been before. However as one can see from the titles noted, foreign genre films are preferred because they have the opportunity to reach broader audiences than the usual foreign film. Genres that reportedly work include: sci-fi, thriller/crime, action, and sophisticated horror. Dramas have had limited success, and comedies often don’t translate, nor does most children’s content. In regard to Cable VOD – foreign box office is becoming an important proxy, because the marketing and pr tend to build US awareness on the larger titles prior to being available here. Many companies have built very successful VOD businesses pursuing a day and date theatrical or DVD strategy. Again, genre films work best, with horror and sci fi being the top performers. 3 of the top 10 non-studio titles in 2010 were foreign language subtitled releases. Small art house distributors say that at most it’s a small dependable revenue stream via services such as INDEMAND http://www.indemand.com (iN DEMAND’s owners are and it services Comcast iN DEMAND Holdings, Inc., Cox Communications Holdings, Inc., and Time Warner Entertainment – Advance/Newhouse Partnership.) Distributors and aggregators all site Time Warner as being far more open to foreign language cinema than Comcast, because it’s urban focused (NY, LA, etc) not heartland focused as Comcast is.
In terms of these titles finding their audiences on Cable VOD, Comcast announced improved search functionality by being able to search by title and Cable VOD is aware of its deficiencies and is said to be improving in terms of marketing to consumers but Cable VOD is still infamous for its lack of recommendation engines and discovery tools. Key aggregators work to have films profiled in several categories and not just the A-Z listing.
Top 25 Multichannel Video Programming Distributors as of Sept. 2010 – Source NCTA (National Cable Television Association)
| Rank | MSO | BasicVideoSubscribers |
| 1 | Comcast Corporation | 22,937,000 |
| 2 | DirecTV | 18,934,000 |
| 3 | Dish Network Corporation | 14,289,000 |
| 4 | Time Warner Cable, Inc. | 12,551,000 |
| 5 | Cox Communications, Inc.1 | 4,968,000 |
| 6 | Charter Communications, Inc. | 4,653,000 |
| 7 | Verizon Communications, Inc. | 3,290,000 |
| 8 | Cablevision Systems Corporation | 3,043,000 |
| 9 | AT&T, Inc. | 2,739,000 |
| 10 | Bright House Networks LLC1 | 2,194,000 |
| 11 | Suddenlink Communications1 | 1,228,000 |
| 12 | Mediacom Communications Corporation | 1,203,000 |
| 13 | Insight Communications Company, Inc. | 699,000 |
| 14 | CableOne, Inc. | 651,000 |
| 15 | WideOpenWest Networks, LLC1 | 391,000 |
| 16 | RCN Corp. | 354,000 |
| 17 | Bresnan Communications1 | 297,000 |
| 18 | Atlantic Broadband Group, LLC | 269,000 |
| 19 | Armstrong Cable Services | 245,000 |
| 20 | Knology Holdings | 231,000 |
| 21 | Service Electric Cable TV Incorporated1 | 222,000 |
| 22 | Midcontinent Communications | 210,000 |
| 23 | MetroCast Cablevision | 186,000 |
| 24 | Blue Ridge Communications1 | 172,000 |
| 25 | General Communications | 148,000 |
FOREIGN LANGUAGE CINEMA VIA OTHER DIGITAL PLATFORMS and REVENUE MODELS:
DTO (Digital Download to Own (such as Apple’s iTunes which rents and sells films digitally) – this space has been challenging for foreign films in the past, and most services do not have dedicated merchandise sections. Thus, the only promo placement available is on genre pages, so the films need to have compelling art and trailer assets to compete. iTunes and Vudu (now owned by WALMART – see below) are really interested in upping the ante on foreign films over the next 12 months. Special consideration will need to be made for the quality of technical materials, as distributors have encountered numerous problems making subtitled content work on these providers.
SVOD (Subscription VOD such as NETFLIX’s WATCH INSTANTLY) – this space is probably the best source of revenue for foreign content because the audience demos skew more sophisticated and also end users are more inclined to experiment with new content niches. Content in this space should have great assets and superior international profile (awards, box office), and overall should evoke a “premium feel” for the right titles, license fees can be comparable to high end American indies. Appetite for foreign titles will increase as the price for domestic studio content continues to accelerate. Genres are a bit broader than VOD/DTO, but thrillers, sci fi and action still will command larger sums ($). Good Festival pedigree (especially Cannes, Berlin, Venice, Sundance, etc.) will also command higher prices. Overall, it’s a great opportunity as long as platforms keep doing exclusive deals. NETFLIX has surpassed 20,000,000 subscribers and a strong stock price and is in a very competitive space and mood again. (See more below). Hulu expects to soon reach 1,000,000 subscribers “to approach” half a billion in total revenues (advertising and subscription combined) in 2011, up from $263 million in 2010. That’s from $108 million in 2009. (see more below)
AVOD (Advertising Supported VOD – such as SNAG and HULU) – Another great space for foreign content (as evidenced by the recent exclusive HULU – Criterion deal – (see below) although that deal is actually for HULU’s subscription service (Hulu Plus). These platforms are more willing to experiment with genres and content types and favor art films and documentaries over genre films. Depending on the film, annual revenues can approach low to mid four (4) figures in rev share. SNAG recently was capitalized to the tune of $10,000,000 but seems to be spending that money on marketing and not on “acquiring” so a film’s revenue is likely to be dependent on performance and rev/share unless one strikes an exclusive deal with SNAG and manages to get an MG. HULU’s revenues are covered above. Films report low 4-figures but sometimes 5 and 6 figure revenues but up until now those higher performing films have been English language and appeal to younger males.
TELEVISION / BROADCAST SALES: For foreign language cinema unless one has an Oscar™ winner or nominee, or an output deal, the prospects of a meaningful license fee are slim. Even worse, if you do secure a deal, it will likely preclude participation in Cable VOD, Netflix and any of the ad-supported VOD platforms such as Hulu and Snag.
KEY SPECIFIC TOP SPECIFIC DIGITAL PLATFORMS / RETAILERS:
AMAZON reportedly is readying a service that would stream 5,000 movies and TV shows to members of its $79-per-year Prime free-shipping membership program. Amazon being corporately tied to extremely popular entertainment information service IMDB and the film festival submission service WITHOUTABOX gives it a potential edge in the market, one that has never been fully harvested but easily could be and seems to be looming. And since its inception, Amazon has let film content providers open up shop on their site directly without a middle-man. Middle man aggregators get slightly better terms. Amazon presently offers 75,000 films and television shows combined and plans to soon exceed 100,000. It should be noted Amazon VOD has been US-focused though recently bought Love Films in the UK.
FOCUS FEATURES’ NEW DIGITAL DISTRIBUTION INITIATIVE: There is not much information out on this yet but FOCUS/UNIVERSAL are launching a new digital distribution initiative that may or may not brand their own channel on iTunes etc., but does seem to be focused on niche cinema to some extent and this may speak to foreign language titles. An option to watch out for.
GOOGLE is working on encroaching into the content delivery market with its launch of GOOGLE TV, which unfortunately has not created quite the fanfare the company planned for. It boasts: The web is now a channel. With Google Chrome and Adobe Flash Player 10.1, Google TV lets you access everything on the web. Watch your favorite web videos, view photos, play games, check fantasy scores, chat with friends, and do everything else you’re accustomed to doing online. GOOGLE TV does come with the Netflix App and others. Google partnered with some of the leading premium content providers to bring thousands of movie and TV titles, on-demand, directly to your television. Amazon Video On Demand offers access to over 75,000 titles for rental or purchase, and Netflix will offer the ability to instantly watch unlimited movies and TV shows, anytime, streaming directly to the TV.
HULU: Hulu’s numbers keep growing for certain films, which has to-date not been foreign language but that may change given the Criterion Collection announcement. Hulu is also now a subscription service (HULU PLUS) and announced the Criterion deal is for that. Criterion of course specializes in classic movies from the canon of great directors–Ingmar Bergman, Jean-Luc Godard, Federico Fellini, etc.–and has about 800 titles digitized so far, many of which are also available via Hulu competitor Netflix. It’s understood that this will be an exclusive deal, and that the Criterion titles that Netflix does offer will expire this year. Hulu Plus subscribers will initially get access to 150 Criterion films, including “The 400 Blows,” “Rashomon” and “Breathless.” Hulu says the movies will run without ad interruptions, but may feature ads before the films start; the free Hulu.com service will offer a handful of Criterion titles, which will run with ads. Hulu, owned by Comcast’s NBC, Disney’s ABC and News. Corp.’s Fox introduced the Hulu Plus pay service last year. Hulu CEO Jason Kilar says the $7.99-per-month offering is on track to reach one million subscribers in 2011. Competing for exclusive content seems to be on the rise as platforms compete for household recognition and top market share.
iTunes (APPLE): iTunes dominated consumer spending for movies in 2010 but that may not last long. One can get onto iTunes via one of its chosen aggregators such as New Video, IODA, Tune Core, Quiver… Home Media Magazine reported the findings of an IHS Screen Digest report that showed that Apple was able to hold off challenges from competitors like Microsoft’s Zune Video (via XBOX Kinect), Sony PlayStation Store, Amazon VOD and Walmart’s VUDU. Despite the new competition, the electronic sellthrough and video on demand market rose more than 60% in 2010, Apple iTunes still came out on top, perhaps due in part to the release of the iPad last spring and Apple TV last fall. Research director of digital media for IHS, Arash Amel, said, “The iTunes online store showed remarkable competitive resilience last year in the U.S. EST/VOD movie business, staving off a growing field of tough challengers while keeping pace with a dramatic expansion for the overall market.” However, it’s important to note that although iTunes staved off competition, the overall iTunes consumer spending fell almost 10% in 2010 to 64.5%. It was 74.4% in 2009. Insiders predict it will not hold its market dominance for long.
Microsoft’s Zune Video was one of Apple’s biggest competitors last year, accounting for 9% of U.S. movie EST/iVOD consumer spending in 2010 but this does not seem a key platform for foreign language cinema.
MUBI: www.Mubi.com having added Sony Playstation to its platforms reach, MUBI now has reportedly 1,200,000 members worldwide and is finally in a better position to generate revenue. Still its own figures estimates amount to 4-figures of revenue and that’s for all its territories. Mubi’s partnership with SONY does not extend into the US.
NETFLIX as reported in Multichannel News “as its subscriber base has swelled, Netflix has become a target for critics complaining that it is disrupting the economics of TV” is now a competitor to Cable and in fact Cable VOD companies won’t take a film if it’s already on NETFLIX’s Watch Instantly service. But Netflix is realizing it erred by losing focus on the independent and is now quietly offering bigger sums that compete with Broadcast offers and that are on par with the 5 and 6 figure revenues generated by Cable VOD for the stronger indie / art house films. Having films exclusively may be the driving force of future monetization in digital, or least in SVOD. Regarding 2011 outlook, Netflix’s “business is so dynamic that we will be doing less calendar year guidance than in the past,” the execs said. For the first three months of the year, Netflix expects domestic subscribers to increase to between 21.9 million and 22.8 million, with revenue between $684 million and $704 million and operating income between $98 million and $116 million. Internationally — meaning, for now, Canada — the company expects 750,000 to 900,000 subscribers with revenue of $10 million to $13 million and an operating loss between $10 million and $14 million.
REDBOX: Redbox, whose brick-red DVD vending machines are scattered across the country, is aiming to have a Netflix-like video streaming subscription service up and running by the end of 2011, company executives told investors mid February. Redbox is a wholly owned subsidiary of Coinstar. The Oakbrook Terrace, Ill.-based company claims to have rented more than 1 billion DVDs to date through vending machines at about 24,900 U.S. locations nationwide, including select McDonald’s, Wal-Mart Stores and Walgreens locations. It should be noted though that Redbox is very studio title focused and wide release focused but its streaming service will likely move beyond that.
WAL-MART bought VUDU and is expected to be a major player. Walmart is the world’s largest retailer with $405 billion in sales for the fiscal year ending Jan. 31, 2010. In the U.S., Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. operates more than 4,300 facilities including Walmart supercenters, discount stores, Neighborhood Markets and Sam’s Club warehouses. VUDU, is Walmart’s recently acquired online media source where consumers can rent or buy movies and TV shows for their internet-ready HDTV, Blu-ray Disc players or PlayStation 3 consoles. Like iTunes, there are no monthly fees. Consumers can buy and rent movies when they want, and 2-night rentals are only $2. It will be interesting to see how VUDU will rise as a contender in 2011 and whether iTunes will suffer as a result of their success. Wal-Mart advertises that regarding VUDU: “from Internet-ready HDTVs to WiFi enabled Blu-ray players, you’ll find all the VUDU ready electronics you’re looking for at Walmart.com. Whether adding a flat panel TV to your dorm room or upgrading your home entertainment center, our selection of VUDU ready HDTVs has you covered. You’ll also save money on our VUDU ready products when you select items with free shipping to your home. With VUDU, you’ll be able to stream HD movies directly from the Internet to your TV in dynamic surround sound for a great low price. Shop VUDU ready HDTVs and Blu-ray players at Walmart.com — and save. “ And the retail giant makes sure all relevant devices / electronics it carries are VUDU-enabled. 2011 and beyond will be telling. Wal-Mart caters to the average American so it remains to be seen if there is an appetite for foreign language film via VUDU in the months and years to come. In its inception VUDU was catering to early adaptors of new technology and those eager to watch HD but now it seems to be becoming more generic. New Video is a preferred aggregator to VUDU, among others.
VODO (Free / monetized Torrent): www.VODO.net: This has not been tried in the US by most distributors if any and not for foreign language cinema but it has worked for several projects such as Pioneer One which generated $60,000 USD by having the content made available for free and then getting donations in return.
Other emerging retailers entering the digital space:
Sears and Kmart are the latest over-the-top threats to pay-TV providers’ video-on-demand businesses. Sears launched its online movie download service, Alphaline Entertainment, which will let Sears and Kmart customers rent or purchase movies, including on the same day they are released on DVD and Blu-ray Disc, provided through digital media services firm Sonic Solutions. Titles currently available to rent or buy from Alphaline include studio and successful TV shows. Under Sonic’s multiyear agreement with Sears, the companies will provide access to Alphaline services through multiple devices including Blu-ray Disc players, HDTVs, portable media players and mobile phones. Sears and Kmart, said in a statement. “We’ll continue to increase the reach and flexibility of the Alphaline Entertainment service by providing consumers on-demand access to the latest entertainment from a range of home and mobile electronics.” Sears, which merged with Kmart in 2005, is the fourth largest retailer in the U.S. The company has about 3,900 department stores and specialty retail stores in the U.S. and Canada. It remains to be seen if they take on foreign language cinema. New Video is also an aggregator to them.
That’s all she wrote folks. Until the next time.
Orly Ravid March 10th, 2011
Posted In: Amazon VOD & CreateSpace, Digital Distribution, Distribution, Distribution Platforms, Hulu, International Sales, iTunes, Netflix, Uncategorized
Tags: Alphaline Entertainment, Amazon, Apple, AVOD, Cinemart, Comcast, Digital Distribution, DTO, film distribution, Focus Features, foreign language film, Google TV, Hulu, InDemand, International Film Festival Rotterdam, iTunes, Kmart, Microsoft Zune, Mubi, Netflix, New Video, PioneerOne, Redbox, Sears, SnagFilms, subtitles, SVOD, Time Warner, VOD, VODO, VUDU, Walmart
NETFLIX vs. Cable VOD & TV – It’s a question of timing
I recently posted on our Facebook page a note about the fact that one has to be mindful about when to initiate a NETFLIX VOD window. Sheri Candler asked to me blog about it. I do everything she says.
We have heard consistently from Cable VOD operators and aggregators and Broadcasters such as Showtime that the Netflix VOD window is considered a cannibalizer of revenue for Cable VOD and TV so know that before licensing rights and resolving windows. When it comes to Netflix they have gotten so successful that they are a more selective platform than Amazon. Amazon wants has recently passed the 80,000 titles mark and is racing to aggregate as many as possible. Netflix has over 100,000 titles on DVD and over 17,000 titles on its streaming service but is now getting more and more selective. Netflix SVOD rights are sold for a flat fee, at least for now. To get onto Netflix, first one has to get on their radar and into their system, and then get that demand up in their queue system to get a good fee offer. One has to then resolve everything else before risking inadvertently killing any chances of a Broadcast sale or Cable VOD distribution. However, depending on the film, you may make more money from Netflix than by selling to let’s say EPIX which will want your Netflix SVOD rights anyway. And you may make more money distributing directly then doing a small Broadcast deal or going with a distributor or aggregator that will take all your digital rights anyway. Though it should be noted most filmmakers cannot get to Netflix directly.
As with anything in film distribution, there is no one rule that applies to all films. This is a case-by-case business. Some films are big enough that one can stagger windows and monetize them all. Some films are better served by being available on all platforms at once or close to it. Some films lend themselves more to rental or ad-supported free-on-demand and others can really generate the transactional (pay per download) business.
The point of this little missive though is just to note the conflation of TV and the Internet is happening. Google TV is here and retailers, Television and device manufacturers, cable operators and telcos are all competing to aggregate and offer as much content as possible. Even print media companies are following suit wanting channels of content on their websites. And soon enough it will be less a discussion of rights and more a discussion of PAYMENT METHODS or MONETIZING METHODS and I think that will always depend on the film and its demographic targets. The options will always be: 1. Ad-Supported / Free on Demand, 2. Subscription 3. Pay Per View 4. Download to Rent, and / or 5. Download to Own. And now instead of focusing on packaged media the focus is is on whether one can play content back on as many devices as one wants and that aspect related to all the various payment methods options. The content providing industries are all racing to aggregate as much content as they can and for it to be playable across as many devices as possible and payment methods vary so far depending on service and distributor choices. Hulu (a platform backed by studios and that was once only ad-supported is now beta testing its Netflix imitation subscription model).
Brands will attract customers just like they always did when video stores were king and just like when you choose which cell phone provider to use or whom to get your Internet connection through, assuming you live in an area with choice.
The other day on a Digital Hollywood Conference panel, I learned a stat from Erik Opeka of New Video: iTunes has 130,000,000 credit cards on file. Some of you are thinking right now, “I’m in the wrong business”.
Orly Ravid October 21st, 2010
Posted In: Amazon VOD & CreateSpace, Digital Distribution, iTunes, Netflix, Uncategorized
Tags: Amazon, Digital Distribution, Digital Hollywood, Epix, Erik Opeka, film distribution, GoogleTV, Hulu, iTunes, Netflix, New Video, Orly Ravid, Sheri Candler, Showtime, SVOD, VOD
TFC Tidbit of the Day 50 Digital Distribution Through an Aggregator
Unfortunately, a great number of key digital platforms must be accessed through the use of an aggregator. Of course there are always exceptions, but the general rule is that to get your films onto Cable VOD, iTunes, Netflix, Hulu, Sony Playstation and other device oriented options and retailer digital platforms , you will have to go through an aggregator or a distributor. We either directly or via partners offer both a commission or a flat fee option (range depends on platforms).
However, you can get onto Amazon directly. Also, you can access DIY oriented ones such as Mubi, Fans of Film and other platforms like them. To the best of our knowledge, more money is made on the key high trafficked platforms, if one can get on them.
Once again we remind you, MARKETING, MARKETING, MARKETING is key to your film’s success no matter what distribution outlet you use.
This concludes our series of tidbits for the time being. As always, if you have questions or need guidance to figure out your film’s distribution path, we would love to hear from you. No rights taken.
Orly Ravid August 27th, 2010
Posted In: Amazon VOD & CreateSpace, Digital Distribution, DIY, Hulu, iTunes, Marketing, Netflix
Tags: aggregator, Digital Distribution, DIY, Fans of Film, Hulu, iTunes, Marketing, Mubi, Netflix, Playstation, VOD