TFC’s Distribution Days is upon us!
Next week, The Film Collaborative is holding a free virtual distribution conference, Distribution Days, which will offer concrete takeaways on the state of indie distribution and how filmmakers can navigate it. Attendees will hear from exhibitors, distributors, consultants, and filmmakers, some with case studies, as they describe and reflect on the landscape.
This conference hopes to help filmmakers develop critical thinking skills around distribution by looking at what is and what is not viable within a traditional distribution framework. It will also offer some alternative approaches. Willful blindness or a doomsday mindset are equally unproductive.
So, we are offering this pre-conference primer to set the tone, take stock of what myths are out there, and talk about what thought leaders in this space are coming up with as ways to deal with the current landscape.
Here we go!
Remember the days when creators and distributors were lying back in their easy chairs, proclaiming their satisfaction with how independent cinema has been evaluated by the marketplace? Yeah, we don’t either…and we’ve been in the industry (in the U.S.) for more than two decades. Nevertheless, there is a pervading sense that the state of independent film has never been worse—and that we’ve been going downhill from this mythic “better place” ever since Sundance was founded in 1978.
Why do we insist on bemoaning a Paradise Lost when the truth is that being a filmmaker has never been a paradise? Filmmakers have always been confronted with predatory distributors, dense and confusing contract language, onerous term lengths, noncollaborative partners, lack of transparency, and anemic support, if any (just to name a few). For an industry that prides itself on creating and shaping stories that speak to diverse audiences, we should be better at articulating truer narratives about our field.
It doesn’t help that, at Sundance this past year, all one could talk about was how streamers were “less interested in independent film than a few years ago, preferring [instead] to fund movie production internally or lean on movies that they’ve licensed” and how Sundance itself was “financially struggling, presenting fewer films than in previous years and using fewer venues.” (https://www.thewrap.com/sundance-indie-film-struggles-working-business-model) Still others like Megan Gilbride and Rebecca Green in their Dear Producer blog have put forth ideas how Sundance should be reinvented completely.
But we all know that independent film isn’t just about Sundance. We have heard a lot of discussion recently about the need to reshape the narratives we tell ourselves regarding the state of the independent film industry.
Distribution Advocates, which is also doing great work chasing the myths vs. the realities of the field, also believes that we must all question “some of our deepest-held beliefs about how independent films get made and released, and who profits from them.”
In their podcast episode about Exhibition, economist Matt Stoller remarked how “weird” it is that even with all the technology we possess connect audiences, we’re still so “atomized” that all that rises to the top is whatever appears in the algorithm Netflix chooses for us in the first few lines of key art when we log in (and we will note that even the version of the key art you see is itself based on an algorithm).
But is it really all that strange? One of the main reasons that myths exist is that someone is profiting from perpetuating them. The same with networks and platforms and algorithms. And the more layers of middlemen and gatekeepers there are, the harder it is for us to see the forest for the trees. Keeping us in our algorithmically determined silos numbs us into not minding (actually preferring) that we are watching things—or bingeing things—from the safety and comfort of our living rooms. The ability to discover on our own content that aligns with our true interests or consuming content in a communal space has disappeared the same way that the act of handwriting has…we used to be able to do it but haven’t done it in so long that it feels unnatural and too time-consuming to deal with.
Brian Newman / Sub-Genre Media acknowledges that the problems remain real, but that what everyone is calling crisis levels seems to him merely a return to norms that were in place before the bubble burst. No one, he says, is coming to rescue “independent film”—certainly not the streaming platforms, which merely used it as necessary to build a consumer base.
Many have posited myriad ideas about how to bypass the gatekeepers. Newman echoed what TFC has been recently discussion internally: that instead of many competing ideas, we need them to be merged into one bigger idea/solution. Like, for example, an overarching solution layer run by a nonprofit on top of each public exhibition avenue that will aggregate data and help filmmakers connect audiences to their content. A similar idea was also discussed at the last meeting of the Filmmaker Distribution Collective in the context of getting audiences into theaters.
By exclaiming that “No one is coming to the rescue,” Brian really means that we are all in this together, and that it’s going to take a village.
We agree, but a finer point needs to be made.
Every choice we make moving forward—whether you are a filmmaker, distributor, theater owner, or festival programmer, what have you—could possibly be distilled into either a decision for the independent filmmaking public good…or for one’s own professional interest. Saying that a non-profit should come in and offer a solution layer to aggregate data is all well and good until it threatens to put out of business someone whose livelihood is based on acquiring and trafficking in that data. How refreshing was it to be reminded at Getting Real by Mads K. Mikkelsen of CPH:DOX that his festival has no World Premiere requirements? It reminds us of the horrible posturing and gatekeeping film festivals do in the name of remaining relevant and innovative. For us to truly grow out of the predicament we are in, some of us are going to have to voluntarily release some of the controls to which we are so tightly clutching.
Keri Putnam & Barbara Twist have an excellent presentation on the progress of a dataset they are putting together of who is watching documentaries from 2017 – 2022. They provide some other data that was very sobering:
Film festivals: comparing 2019 numbers to 2023 – there was a 40% drop in attendance;
Theatrical: most docs are not released in theaters and attendance is down even for those that are released.
But they also note that there is really great work being done in the non-theatrical space— community centers, museums, libraries – that is not tracked by data. TFC’s Distribution Days offers two sessions on event theatrical and impact distribution, so we’ll be able to see a tiny bit of that data during the conference.
We also know that the educational market is still healthy, and that so many have remarked of the importance of getting young people interested in film…so we have three sessions where we hear from the Acquisitions Directors of 11 different educational distributors.
We also have a panel from folks in the EU who will provide advice on the landscape and how best to exploit films internationally and carve our rights and territories per partner. And we’ll speak to all-rights distributors about what kinds of films they see doing well, what they are doing to support filmmakers—and what their value proposition is in this marketplace.
We have a great panel on accessibility, and two others that relate to festivals and legal agreements.
Starting off with a keynote from noted distribution consultant and impact strategist Mia Bruno, the 2-day conference aims to summarize the state of the industry while providing thought provoking conversations to inspire disruption, facilitate effective collaboration, and to aid broken hearts.
Regardless of whether current days are better or worse than the heydays of Sundance and the independent film of yesteryear, Distribution Days will identify the current obstacles of the independent film distribution landscape, and what we can hold on to—as a commonality—to evolve the landscape together in the future.
If you look a little deeper, you will see that, despite all the challenges, filmmakers have and can still achieve “success” when they understand the terrain, (sometimes) work with multiple partners with a bifurcated strategy, protect themselves contractually, and maintain and grow their own personal audience.
We hope you will join us. And for those of you that cannot make all of the sessions we are offering live on May 2 & 3, you’ll be able to catch up on what you missed via The Film Collaborative website after the conference is over.
We look forward to seeing you next week! And if you have not registered yet, you can do so for free at this link.
David Averbach April 25th, 2024
Posted In: case studies, Digital Distribution, Distribution, Distribution Platforms, DIY, Documentaries, education, Film Festivals, International Sales, Legal, Marketing, Theatrical
Best Advice For Marketing an Independent Video Project
Last month, TFC invited a select group of Los Angeles-based filmmakers to share their knowledge and specific details about how they marketed and distributed their independent films. We learned a lot and we thank those who took part that day. Now, we want to open up this opportunity to all creators, whether you make features, short films, or web series, so that we all may learn from each other in an anonymous, but factual way.
We know, many other entities have tried to compile statistics and details and have invited independent creators to contribute, but we think a lot of that information has been less than forthcoming or distributed within only a small subsection of creators who participate in closed labs or mentoring sessions. We propose to do something different.

For the next month, we are asking any creator who has actually participated in the marketing and distribution of their project (this is a requirement) to come forward and fill out this 10 question survey in detail. No questions will be asked about the identity of the creator or of the project which should allow participants to be completely honest about their efforts and results. The results will be compiled into a whitepaper of best practices and charts showing budget levels and revenue levels that will benefit the creators operating in this turbulent and confusing period of plenty of consumer choice, but creator uncertainty about the financial viability of their work. The whitepaper will be published online, for all to download for free.
We sincerely hope you will agree to help us, all of us, by participating. Our aim is to have the whitepaper ready for distribution by the beginning of the new year. TFC mailing list members will be notified first, so if you want a first look, please join that list here. Everyone will have access via this blog once the document is published.
We’re really excited to learn what creators are doing and we know you will find their insight invaluable. Thanks for participating!
Sheri Candler September 11th, 2017
Posted In: case studies, Distribution, Marketing
Tags: film budget, film distribution, film marketing, film revenue, survey, The Film Collaborative
How viable is DIY Digital Distribution? The Case Study of Tab Hunter Confidential
David Averbach is Creative Director and Director of Digital Distribution Initiatives at The Film Collaborative.
When distributing your film, a lot of time is spent waiting for answers. Validation can come only intermittently, and the constant string of “no”s is an anxiety-ridden game of process of elimination. Which doors open for your film and which doors remain closed determines the trajectory of its distribution, whether it’s festival, theatrical, digital, education or home video (until that’s dead for good).
I work with filmmakers, way down-wind of this long and drawn-out process, who, after exhausting all other possibilities, have “chosen” DIY digital distribution as a last resort.

TFC’s DIY digital distribution program has helped almost 50 filmmakers go through the process of releasing their film digitally over the past 5 years and with most of them, I have often felt as though I were giving a pep-talk to the kid who got picked last for the dodgeball team. “Hang in there, just stick to it…you’ll show them all.”
Is DIY Digital Distribution anything more than a last resort? Perhaps not…
DIY vs. DOA
Since TFC was formed over six and a half years ago, we have optimistically used “DIY” as a term of empowerment, where access and transparency had finally reached a point where one could act as one’s own distributor. After all, we tell these (literally) poor, exhausted filmmakers, “no one knows your film better than you do”, so “no one can do a better job of marketing it.” With a little gumption, a few newsletters and handful of paid Facebook posts, you, too, might prove all the haters wrong and net even more earnings than Johnny next door who sold his film to what he thought was a reputable distributor but never saw a dime past the MG (minimum guarantee) in his distribution agreement. We even wrote two case study books about it.
It’s not that I’m being untruthful with these filmmakers. Nor is it the case that these films are necessarily of poor quality. What they have in common is a lack of visibility. Most had some sort of festival run, and only a handful were released theatrically, usually with one- or two-day engagements in a handful of cities. Occasionally, we’ll get a film that has four-walled in New York or Los Angeles for a week. Or sometimes ones that have played on local PBS affiliates or even on Showtime. But their films are not even close to being household brand names. So without the exposure or the marketing budget, they can do little more than to deliver their film to TVOD platforms like iTunes and hope for the best.
So what happens to these films? The news, as a whole, is not good. Based on what I’ve seen from these films in the aggregate, and all things being equal, if you DIY/dump your film onto only iTunes/Amazon/GooglePlay with moderate festival distribution but no real money left for marketing, you will be lucky to net more than $10K on TVOD platforms in your film’s digital life.
And the poorer the filmmaking quality of your film, or the less recognizable the cast, or the less “niche” your film is, the more likely it will be that you won’t even earn much more revenue than what is required to pay off the encoding and delivery fees to get your film onto these platforms in the first place (which is around $2-3K).
Which is why, as of late, I’ve been aggressively suggesting to filmmakers that holding off on high profile TVOD platforms and instead trying to drive traffic to their websites and offering sales and rentals of their film via Vimeo On Demand or VHX, two much cheaper options, might be a better use of their limited remaining funds.
But am I down on DIY? Not necessarily.
Risky Business
Granted, there are a lot of films out there for which The Film Collaborative can do very little for in the area of digital distribution other than hold filmmakers’ hands. But what about for films working at the “next level up” from last-resort-DIY? Films who have either gotten a no-MG or modest-MG distribution offer?
Many distributors and aggregators working at this level will informally promise some sort of marketing, but many times those marketing efforts are not specifically listed contractually in the agreement. So when filmmakers ask me whether going with a no-MG aggregator is better than doing DIY, this is my answer…
It’s important to remember that, once a film is on iTunes, no one will care how it got there. And by this I mean with no featured placement, just getting it on to the platform. So, if that’s all a distributor/aggregator is doing, this is not the kind of deal that a filmmaker can dump into someone else’s hands and move on to their next project. In fact, many aggregators will send you a welcome packet with tips and suggestions on how to market your film on social media, such as Facebook. In other words, they are literally expecting you to do your own marketing. Not just do but pay for. So, it is entirely possible that all that an aggregator or distributor is doing is fronting your encoding costs, which they will later recoup from your gross earnings, but only after they take their cut off the top. And if your distributor is offering you a modest MG, you must be prepared for the possibility that that MG may be all the earnings you are ever going to see. Certainly, we have seen many, many filmmakers in this position.
So the question remains: Is DIY still too risky for all but films that have run out of options?
It’s a hard question to answer, mostly because there is no ONE answer. Undoubtedly, some films will be helped with such an arrangement and some films will not.
A View from the Other Side…
Distributors, of course, will stick to the sunny side of the street. They will tell you that DIY is too risky for the vast majority of films, and remind you that distribution is more than getting a film on to one or two platforms.
When I asked Gravitas Ventures founder Nolan Gallagher, a veteran in distribution and whose co-execs have a combined 50+ years in distribution experience, about his feelings regarding DIY, he was quick to point out that the main difference between a proven distributor and DIY is that while much of the work in DIY happens in year 1, distributors can help in year 3 or year 5 or beyond. He believes that DIY individual filmmakers will be shut out from new revenue opportunities (i.e. the VOD platforms of the future) that will be launched by major media companies or venture capital backed entrepreneurs in the years to come because these platforms will turn to established companies with hundreds or thousands of titles on offer.
This is a fair point, in theory, but I honestly cannot recall a single instance of one of our filmmakers from 2010-2013 jumping for joy over that fact that his or her distributor had suddenly found a meaningful new VOD opportunity in years 3-5, nor have we heard of any specific efforts or successes down the line. But it’s good to know one can expect this if signing with a distributor.
He also mentioned that many of Gravitas’ documentarians receive multiple 5 figures in annual revenue over 5 years after a film first debuted.
That’s nice for those filmmakers…But what about the ones that don’t? It would be ludicrous to suggest that any decent film, with the proper marketing and industry connections, can become a respectable grosser on iTunes.
By no means am I singling out Gravitas in order to pick on them in any way. For many films, clearly they do a terrific job.
But does that mean that there aren’t a handful of filmmakers that have gone through aggregators like Gravitas or other smaller distributors that many TFC films have worked with, such as The Orchard, A24, Oscilloscope, Virgil, Wolfe, Freestyle Digital Media, Breaking Glass Pictures, Amplify, Wolfe, Zeitgeist Films, Dark Sky Films, Tribeca Films, Sundance Selects, who are not entirely convinced that they were well served by their distributor? Of course not.
The Million Dollar Question…
The question I really wanted to know was more of a hypothetical one than one that assigns blame: if these so-called “borderline films” that went through aggregators/distributors had done DIY instead, how close could they have come netting the same amount of earnings in the end? Is it possible that they could have gotten more?
This is a hard question—or, should I say, a nearly impossible question—to answer, because no one has a crystal ball. But also because of the continued lack of transparency surrounding digital earnings, despite initiatives like Sundance Institute’s The Transparency Project, and because the landscape is continually evolving.
A recent article in Filmmaker Magazine, entitled “The Digital Lowdown,” discusses how independent filmmakers struggle to survive in an overcrowded digital marketplace and “admits” that niche-less festival films will only gross in the range of $100K-$200K, and that, in fact, talks about a “six-figure goal.” But in almost the same breath, there is a caveat. Sundance Artist Services warns that “…if a filmmaker spends about $100,000 in P&A to finance a theatrical run, they’re probably going to be making that much from digital sources.”
I have heard many stories of distributors and filmmakers alike, who put “X” dollars combined into P&A for both theatrical and digital only to make a similar amount back in the end. So what’s the point? If you look at distribution from the perspective of paying back investors, are a good portion of filmmakers netting close to nothing, no matter whether they do DIY or whether they gear up for a theatrical and digital distribution via a distributor? If a film does not succeed monetarily, is the consolation prize merely visibility and exposure? (Which is not nothing, but it’s not $$ either).
Sweet/Talk
A few months ago, my colleague Bryan Glick posted a terrific piece on our blog that questioned the ROI of an Oscar®-qualifying run, given the unlikelihood of being shortlisted. Bryan implies that because filmmakers like hearing “yes,” and like having their egos stroked, when publicists, publications, screening series, cinemas, and private venues all lure filmmakers with a possibility of an Oscar®, something takes over and they lose perspective at the very moment they need it most.
Could the same be true for a distribution strategy? Are filmmakers so happy to be offered a distribution deal at all that they are unable to walk away from that distribution deal, even if they suspect that it undervalues their film? And could a viable DIY option change that?
Evaluating Success with DIY
Last fall, I began to think about what a “successful” DIY digital release could look like. On the low end, we’ve heard about a magical $10K figure that I discussed above…in the context of MGs paid to Toronto official selections via Vimeo on Demand, and Netflix offers to Sundance films via Sundance Artists Services. So it would have to be at least greater than $10K. And on the high end, it would have to be at least $100K that the filmmaker gets to net over a 10-year period.
Working backwards, how can this be achieved and is it possible to recreate that strategy via DIY?
One thing that gave me hope was when my colleague Orly Ravid, acting as sales agent, negotiated a licensing low-six-figure deal with Netflix for the film Game Face, about LGBTQ athletes coming out. The film won numerous audience awards at film festivals, but had no theatrical release. Timing, as well as the sports and LGBT niche, made this film perfect for a DIY release. The only catch was the Netflix insisted on a simultaneous SVOD & TVOD window, so Netflix and iTunes releases started within one day of each other. TFC serviced the deal through our flat-fee program via Premiere Digital Services.
Lessons Learned from the DIY Release of Tab Hunter Confidential
 This past Spring, TFC spearheaded the digital release of Tab Hunter Confidential, a film for which we also handled festival and theatrical distribution, as well as sales. Truth be told, this film almost went through a distributor. In the end, however, after a protracted period of negotiation, an offer was made, but knowing how much Netflix was willing to offer, Orly advised the filmmaker to walk away from the deal and try our hand at a DIY release. The filmmaker agreed, and we serviced the Netflix deal via Premiere. However, as Netflix wanted the film for June, which is Gay Pride Month, we had a limited amount of time in which to do iTunes, and I was determined to make the most of it.
This past Spring, TFC spearheaded the digital release of Tab Hunter Confidential, a film for which we also handled festival and theatrical distribution, as well as sales. Truth be told, this film almost went through a distributor. In the end, however, after a protracted period of negotiation, an offer was made, but knowing how much Netflix was willing to offer, Orly advised the filmmaker to walk away from the deal and try our hand at a DIY release. The filmmaker agreed, and we serviced the Netflix deal via Premiere. However, as Netflix wanted the film for June, which is Gay Pride Month, we had a limited amount of time in which to do iTunes, and I was determined to make the most of it.
So what were the goals? And how could we get there?
I had been trolling both the “Independent” and “Documentary” sections on iTunes for months in preparation for what has now become this article on DIY. I had been noticing that while it is easy to get a film into the “New & Noteworthy” section in “Documentaries,” which contains at hundreds of films, the similar section in “Independent” is limited to about 32. So how could one get there? And how could one’s film be featured in the top carousel in “Independent” or in any of the genre categories? Would it help to offer iTunes exclusivity? Would it help to do iTunes Extras? Could we contact Apple and try and schedule something? What else could be done? These are the questions that I set out figure out on my own, or to ask our aggregator, Premiere Digital Services.
How can I get my film to be one of the 30+ films in the “Independent” Section of iTunes? This section is populated at Apple’s discretion. Their iTunes division is based in L.A., not Silicon Valley, and they attend film festivals and are very up-to-date on the indie film landscape. It’s clear, however, that while they do speak with distributors and aggregators about what’s coming down the pipeline, most of the decisions about what is to receive placement in this section occur within a week or two of the release date in question, and are decided ultimately by iTunes. I informed Premiere Digital that we were very interested in being placed in Independent, and they told me that they have weekly calls with iTunes and that—closer to the date of release—they would mention the film to them. In the end—spoiler alert—we did manage to get Tab into this section. But there were no back room deals to get that to happen…so I can hereby confirm that it is possible to be featured on the iTunes store based solely on your film and the specifics of its release.
Rotten Tomatoes Score: Out of approximately 100 films that appeared from late November 2015 to early February 2016 (which I kept track of manually, so the following is not completely scientific), about 50 of those had a “fresh” rotten tomatoes score. About 40 of those 50 had RT scores over 80%, and many of those were Certified as Fresh. Of the remaining 50 films, about 20 had “rotten” RT scores, and about 30 had no score at all. Luckily, Tab Hunter Confidential has an RT score of 87%, so I knew I was safe from that perspective. But while I was investigating, I was particularly interested in those films without a score. I noticed that many of them had star power attached, and a few of them were holiday-themed. A few of them were Lionsgate titles. And a few sports-related and horror titles, which always seem to rise to the top. I glanced at the Independent section for this week (third week in August), and these numbers pretty much bear out, save the holiday ones. The takeaway here was that if your film did not have a theatrical (and therefore perhaps does not have a RT score), if it doesn’t have famous people in it, it’s not about sports or is not in the horror genre, your chances of appearing in this section as a DIY film going through an aggregator seem pretty slim.
Check in, check out dates. As many of you know, films always end up in one of Apple’s genre sections. They stay there a few weeks or even a few months until they are bumped out of that category by newer items. But those sections are very glutted. The “Independent” section is a second placement, one that is curated by Apple, of only three rows of films. One thing that I became acutely aware of was the high turnaround in this section. Films seemed to be refreshed twice a week: once on Tuesdays (release day), and then again on Fridays. This was more or less consistent, although I got the feeling that on a few occasions things were a bit early or a bit late.
At any rate, it was very clear that if films were not pulling their weight, they would be booted from the “Independent” section for something else. At least 1/3 of the films were gone after only a few days. After all, Apple is in the business of making money off these films too. What occurred to me is that if filmmakers are doing distribution deals to get placement, and their films only last 3 days in the “Independent” section, and that measly placement is what amounts to the big perk/payoff of going through a distributor, it’s a pretty sad day for either the filmmaker, the distributor, or both.

How can I get my film featured in the top carousel? It turned out to be the same answer as for the Independent section in general, but I can admit it now…I was a pest: I asked multiple people at Premiere this question. I was told over and over that Apple will make a request for layered artwork if they are interested in featuring the film. Two weeks before the release date I had not heard anything. But less than a week before, Premiere received the request for artwork from Apple. We ended up being featured in both the “Independent” and “Documentary” sections.
Why did they pick us? I am not completely sure, but here are my guesses: We had a great film festival run. The film was based on a bestselling book. We had a high RT score; we did a 40+ city theatrical; we had a lot of press, and we had a publicist; the film was apparently not doing terribly in the iTunes Pre-Order section, Tab Hunter did many interviews when the theatrical came out; Tab Hunter is freaking Tab Hunter; the film spans both LGBT genres and the genre of women of a certain age who came of age in the 1950s and still remember Tab’s poster on their bedroom walls; the artwork was classy; it was almost June; we gave them an exclusive (although I don’t think they ever advertised it as such); we did an international release on iTunes (we were told that Apple likes films to have more than one territory to be featured, which is kind of strange, because it wasn’t featured in any other iTunes store, like Canada or UK); and lastly, we did some iTunes custom artwork and iTunes Extras.
Walking the walk. Speaking of customization, one thing that I noticed about every film in the “Independent” section was that most detail pages contained customized promotion background artwork. Apple likes this. It gives the film branding, credibility. Apple has two different kinds of background art one for the iTunes store and one for AppleTV. We opted to do just the iTunes store art, which is an extra $75 conformance fee at Premiere. We also did iTunes Extras basic package, for about $700 extra, which offers a chance to include bonus features, such as outtakes and other exclusive video. Since we were planning on including bonus interviews on our DVD, we included that file, as well as 10 minutes of interviews for which iTunes is the only place that they are available. I’m not sure if Extras helped the featured placement, since we were literally down to the wire on having them appear on the store in time for the release. (At the last minute, we needed a looping background audio for iTunes, which we didn’t realize was mandatory, so if you go the Extras route, don’t forget that that audio file is needed).
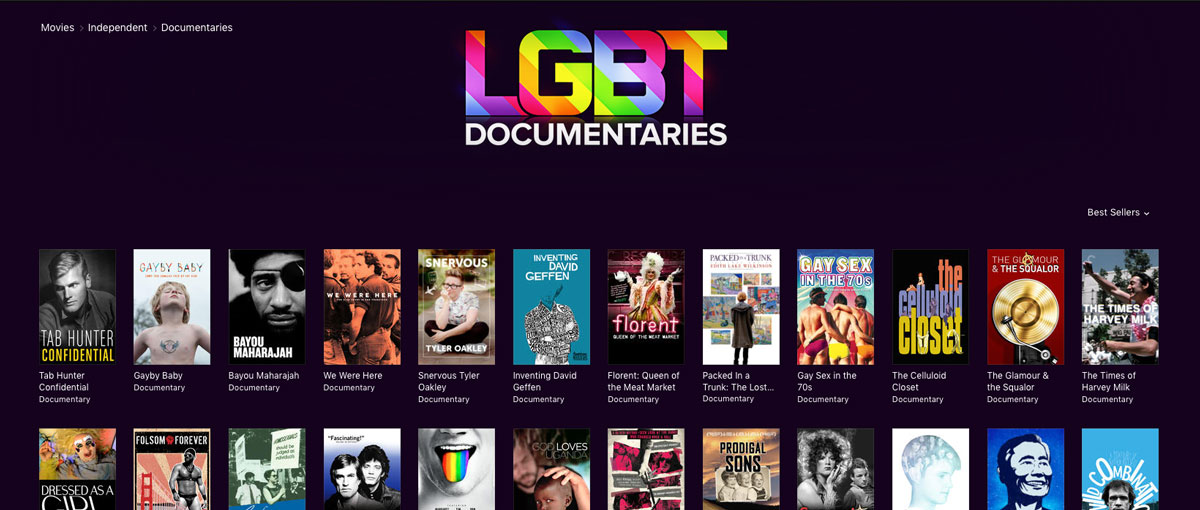
Results. All in all, we did everything we could, and it paid off. We were featured in both the carousels of the “Independent” and “Documentary” genre sections, and stayed in the “Independent” carousel for a full week and in “Documentary” carousel for two weeks. We stayed in the “New & Noteworthy” part of “Independent” for several weeks. At its peak, we reached #2 in Documentaries, being surpassed only by Michael Moore’s Where to Invade Next, which months later is still in the “New & Noteworthy” part of “Independent.” We made sure Tab Hunter Confidential shows up in both the iTunes Extras section and the “LGBT Movies” Collection section. The more places to find the film, after all, the more chance of it being rented or purchased.
After over 3 months, around the third week of August, Tab Hunter Confidential was the 12th All-Time Bestselling LGBT Doc in the iTunes store. As of the date of this blog, it has dipped down the 14th. It is still in the “New & Noteworthy” part of “Documentaries,” although to be fair that section contains hundreds of films.
Regrets? Could we have stayed longer in the iTunes carousels? Two things worked against us. First, although there was a social media push when the film was released, it was pretty limited, as we had only a small P&A budget. With more of a spend, we could have gotten more attention during the second week, and perhaps sales would have warranted the film sticking around for longer. Other films, such as Gravitas’ Requiem for the American Dream, for which TFC handled the Theatrical, featuring Noam Chomsky, have done a much better job surfing this wave. Fortuitous timing with Bernie Sanders, but that is a story for another day.
Although we offered TVOD exclusivity to Apple until June, it was unclear whether they really cared about that, as they never promoted it as such, and we probably should have released on Amazon, GooglePlay and Vudu on the same day as iTunes.
(Speaking of Amazon and GooglePlay, I once asked someone who used to work at Premiere how one gets featured on those other platforms’ stores. What they told me was shocking: Amazon and GooglePlay basically copy content ideas from the iTunes store. This was about a year ago, so who knows if this is still happening, or if it was even true at all. But I was kind of blown away by this.)
Conclusion. There are undoubtedly things one could immediately try and recreate from the steps that were taken with Tab Hunter Confidential. However, who is to know if they could work a second time, with a different film and different timeframe?
I am not suggesting in this article that distribution deals are unnecessary. Many companies have a ton of industry connections and experience that one might not be able to recreate with DIY.
But in this case, the filmmaker is thrilled, and my TFC team believes that dollar for dollar, the filmmaker walked away with a guaranteed net that is more than they would have received had they taken the distribution deal that was offered to them by a distributor.
So should DIY be considered a dirty word? Only you can decide if it is right for you film. As a whole, the jury might still be out, but, at the very least, I suspect that we’re going to get more filmmakers interested in iTunes background art.
Be sure to look out for Tab Hunter Confidential, on digital platforms, and now on DVD and Blu-Ray, which have recently been released by our friends at FilmRise.
David Averbach September 6th, 2016
Posted In: Amazon VOD & CreateSpace, case studies, Digital Distribution, Distribution, Distribution Platforms, DIY, education, iTunes, Marketing, Netflix
Are DVDs Worth It For DIY Film Distribution?
We are gearing up for a big article on DIY Digital Distribution, which will be posted very soon. In the meantime, we liked this No Film School case study article on DIY DVD Distribution so much that we had to link to it on our blog as well as SM. Enjoy!
Orly Ravid August 17th, 2016
Posted In: case studies, Distribution, DIY
An Update on International VOD Opportunities Outside the U.S. in The Indie Film Sector
Guest blog post by Wendy Bernfeld

The Cannes Film Festival starts today, and any Cannes season would not be complete without an update from our dear friend and colleague Wendy Bernfeld, Founder and Managing Director of Rights Stuff and co-author of our second case study book in 2014 Selling Your Film Outside the U.S. (free on Amazon Kindle and Apple iBooks. Wendy specializes in Library and Original Content acquisition/distribution, international strategy / deal advice, for traditional media (film, TV, pay TV), digital media (Internet/IPTV, VOD, mobile, OTT/devices), and web/cross-platform/transmedia programming, and also active on various film festival / advisory boards, such as IDFA, Binger Film Institute, Seize the Night, Outdoor FilmFest, and others, including TFC! Follow her on Twitter: @wbernfeld.

What’s happened out there in the two years since TFC first published Selling Your Film Outside the U.S. (“The Book”)?
My introductory chapter to the book, entitle, “Digital Distribution in Europe” provided a snapshot of the evolving sector at that point in time. However, by now, the sector, particularly in the area of SVOD and AdVOD, has leaped even more forward, and includes more mature services as well as new niche and thematic services out there— as well as some services with an increased appetite for foreign language, art house and documentary films/series (finally).
A. Blurred Lines — Traditional vs. Digital — Hybrid Platforms
More recent trends 2015-16 include increasingly blurred dividing lines between so-called traditional vs digital players .
- Traditionals: Many traditional players, internationally, (like telecoms, cable and free tv) have now become more digital, by either 1) bysetting up their own competing, or complementary, multi-window VOD offerings such as SVOD services (e.g. Channel 9’s STAN in Australia or Liberty Global’s MyPrime in both Switzerland and Netherlands); or 2) electing to instead “sleep with the enemy” by just hosting digital channels like Netflix, Spotify, etc. on their set-top box (e.g. Orange, ComHem Sweden, Virgin UK). Some traditionals opt to distinguish the brand identity of the VOD service from the main service, (different names); while others unite both services under one brand, such as CanalPlay (C+) or Viasat’s VIAPLAY. Recent developments include BBC announcing it will start SVOD internationally, after also migrating its Channel 3 to digital-only online offering; and ITV starting CURIO, a nonfiction SVOD in the UK.
- Digitals: Correspondingly, the so-called formerly digital-only players like Netflix, Amazon (previously more complementary or second window) are now acting a great deal like the traditional players. Think: old-fashioned commissioning broadcasters who increasingly require first-window status and exclusivity, and who are funding “originals”, getting involved competitively commissioning films from development stage etc. and fashioning game-changing windows.
Despite the complexity, this is overall great news for creators/rights-holders since it allows even more opportunity to maximize revenues and audiences per successive window, platform and region, if one takes the time to do it right.
B. VODs Per Window:
Lets look at various platforms in each window today, from TVOD, DTO, through to SVOD, AdVOD, etc. Note that many deliberately offer MULTI-model consumer services – such as Orange, Canal Plus and BSKYB (TVOD/DTO, SVOD), Amazon (Instant and Prime, for TVOD/DTO and SVOD, respectively) and Wuaki – while others (Netflix and Curio) operate under just one consumer business model.
- TVOD/DTO:
- For the Big5 (Google, Amazon, iTunes, Xbox, PS), one still generally goes through a digital aggregator, like Juice, Cinedigm, Kinonation, and Syndicado in N.America. Outside N.America, EMEA counterparts in include one of Rights Stuff clients MOMEDIA (attractive multi-platform new biz model, lower cost for more platforms and combined with social media/marketing) – and others like DoCo/ODMedia (NL), MoviePartnership, and Under the MilkyWay.
Shop around…these aggregators they have different models and price alone shouldn’t be the only indicator. Also look at their marketing/positioning: some take your IP, others (like Rights Stuff, TFC) do not.
- Going direct to the others in TVOD/DTO:
Don’t stop at one or even all of the Big5. The play is to have multiple deals , non exclusive, staggered, in all the windows, in each region. Virtually every country has an active telecom and cable or DTH competitor in the region, as well as mobile and online /consumer electronics players who offer VOD, so licensing non-exclusive TVOD to them on top of others is a good first step in the chain.Beyond the utility companies, some other examples in TVOD/DTO include premium pay tv services or platforms like CanalPlus (France and other regions) and BSkyB, (UK, Germany, Italy, New Zealand). Also theatrical chains in some countries, such as Cineplex in Canada or Pathé in Holland, have VOD arms and thus can offer complementary marketing of films in theatrical window with the subsequent TVOD/DTO window. Also check out online VOD indie film specialist FilmDoo (well-curated indie/art house focused, now in UK/EIRE and soon expanding), and as earlier written, Curzon offers day-and-date theatrical combined with VOD in UK. Wuaki announced moves into 15 countries internationally by end of 2016, most are now TVOD/DTO but the Spain HQ is an SVOD OTT platform. The NFB in Canada started TVOD/DTO in N.America and recently in 2016 an SVOD service, and they now buy docs/films from other sources and regions, too.
- Deals: TVOD/DTO continues to be typically a rev share model and sometimes only a loss leader, but can help drive critical awareness, especially when accompanied by social media marketing and audience engagement strategies. Sometimes, film dependent (for eg if a very niche film) it saves money to skip the big5 (who require costly specs) and license direct to the other international tvod/dto platforms, as then at least one participates from day one in revenues, vs having to recoup expensive deliverables.
- For the Big5 (Google, Amazon, iTunes, Xbox, PS), one still generally goes through a digital aggregator, like Juice, Cinedigm, Kinonation, and Syndicado in N.America. Outside N.America, EMEA counterparts in include one of Rights Stuff clients MOMEDIA (attractive multi-platform new biz model, lower cost for more platforms and combined with social media/marketing) – and others like DoCo/ODMedia (NL), MoviePartnership, and Under the MilkyWay.
- SVOD/PAY – whether first and second windows:
As predicted, this window has so far overall been most remunerative since it’s usually structured by a flat fee license fee (although smaller or niche thematic platforms in the larger USA market (such as Fandor or Indieflix) are still offering just a revenue share formula, which can make the returns lackluster). We generally favor licensing to platforms that pay even a modest flat fee, upfront. Or in some cases in the ‘’back end’’ i.e. rev share to start, then if the revenues at the end of a year (or the window) don’t reach, say, $1000, the platform pays the difference. That sort of model can be attractive for startup platforms who truly believe in the power of their SVOD service but are cash-strapped at the start. So one can license to a less remunerative platform, which does a great job of curation, editorial, placement, and
also license other SVOD platforms who may be more remunerative for you. - In the USA, you’ve finally seen growth since 2015 in the SVOD sector for documentaries, including the Curiosity Stream SVOD OTT platform (by former Discovery founder, John Hendricks), whose programs tend towards educational and traditional. They are usually on a rev-share only model, whereas competitor xive.tv (SVOD OTT) also buys docs features/series, but over a wider range of topics including more populist/reality content- and xive.com works on a flat fee and/or combo deal model. And a deal with well-curated xive.tv delivers an extra ‘lift’’ in reach by providing carriage on other platforms (Hulu, Roku, Amazon, etc.).
- In EMEA/beyond, some other SVOD OTT platforms for docs and arthouse have arisen such as CURIO in UK (via ITV), Filmin (Spain, Portugal, Mexico). Mobil has now transformed its model to a curated daily film+library, a lower price and is complete with hefty investment by Chinese backers/reach into China. They also started paying some flat fees, or MGs, for select higher-end indies, as opposed to the pure rev share SVOD model of earlier days.
There’s been a surge of local SVOD players popping up to compete or complement as Netflix or Amazon/competitors rolls into each new region. Some present outright competition, engaging in bidding wars for similar mainstream content offerings and price points. For instance, MNET South Africa, a premium pay tv operator, launched ShowMax locally and soon after announced further expansion. Other examples include: Videoland Plus (owned by free tv RTL/& SBS channels in the Netherlands) and Maxdome (owned by Prosieben in Germany).Others are complementary SVOD services, offering older library services in general interest. And still others exist at lower price points in narrow verticals/themes, like kids, anime, arthouse, etc. Hopster (UK/USA) is a buyer of purely kids programming, recently launched also in Iceland on Vodafone platform; similar to MinBIO (Nordic kids), which buys from international producers as well as from studios or locals, and Kidoodle (Canada svod ott). Cirkus in Nordic focuses on best of British programming (SVOD OTT).Recently in 2016 there’s a raft of SVOD platforms in developing regions like the MidEast and South East Asia: such as multi-region IFLIX and ICFLIX. As before Australia has pay and svod services such as Foxtel’s Presto (Australia); Lightbox (New Zealand), and Stan (channel 9).SVOD Deals: Producers should usually seek flat fee, but some platforms perform well on rev share. Particularly if you license multiple platforms in the same window and cross-promote so consumers find you from whichever entry point. In the lucky case where you can play off one against the other (e.g. traditional pay tv vs SVOD first-run) a stronger case can be argued for the license fees, as the buyer is “not the only game in town” anymore. In other cases, non-exclusive, multiple-platforms deals in smaller amounts still add up the revenues and audience. Prices can range from €250-2000 for an indie doc of film if old library and yet also up to 5- and 6-figure sums if a higher-end indie/doc or original/first-run. Pricing is also obviously affected by volume of the films in a deal, the number of regions, the awareness (platform, audience), popularity, critical acclaim, and language and cultural portability. - ADVOD:
Although TubiTV/AdRise in USA and Hulu (multi-model in AdVOD and SVOD) are strong platforms offering solid returns to producers in the AdVOD sector, there aren’t many doing the same in EMEA. Here, again, it’s worthwhile to have your films spread on other free AdVOD platforms (vs pirate sites) so the returns are cumulative and there’s cross-promotion. Sometimes a film sampled on AdVOD can help to yield revenues from DTO (e.g. if a consumer discovers a lesser known film on an AdVOD platform and decides then to buy it on iTunes, while they’d not have bought it unknown before).Some updates on the AdVOD sector in EU: Viewster.com (27 countries in EMEA) has shifted focus (since our last reference in the book) from buying arthouse/festival films, to millennial content, including edgier, fast-paced docs, some originals and anime. In 2015 they had added an SVOD anime service, but in March 2016 shut it down, as others have become more aggressive in that space. DailyMotion, EU competitor to Youtube, were sometimes paying flat fees and sometimes commissioning series, but a recent sale by Orange to Vivendi may bring changes. Channel4 (UK) recently launched WalterPresents, an AdVOD site focused specifically on dramatic series and some films strictly from outside the UK.
- HOW TO REACH THE PLATFORMS:
As before, one goes via aggregators for Big5, but your agent/representative, or distributor/sales agent, OR YOU YOURSELF can hit up the others direct.REPS: I highly recommend interviewing your potential sales agent/distributor, with new questions such as asking 1) if they’ve been active in digital lately vs just their traditional buyers; and 2) if so, then with which types of platforms—Big5-7 or also beyond to International? If not, it doesn’t have to be a barrier, if they’re willing to allow nonexclusivity in digital, and/or to allow you or digital agents to assist and collaborate alongside.
- FUNDING (including by SVODs):
Although beyond the scope of this article, note In 2015-16 there’s been increased activity in 5-6 figure prebuying/funding of originals or premieres (film, series)—not just from English regions and not only via Netflix and Amazon, but also other international and EMEA services like OneNet Poland, IcFlix, Telenet, KPNPlay, Vimeo, Vivendi/Canal+, etc.On the Amazon front, aside from bigbudget originals via Ted Hope’s division such as ChiRaq at Berlinale and Woody Allen this Cannes, they also fund weboriginals, digital series, via prototyping schemes and audience involvement/feedback. Netflix has been intensely active in funding originals, including docs and nonfiction (while a few years ago that was a rarity); more deals in arthouse, docs and foreign will be announced at or after Cannes.In Canada there is a funding for coproduction in digital programs; And in France/EU, Vivendi (owner of Canal+ and DailyMotion) just in April 2016 launched its “Studio+” initiative &,dash; funding short-form original series for mobile and telecom operators.
- TAKEAWAYS
As before in the 2014 Book, the following have intensified:
- Act quickly and work collaboratively (filmmakers + agents/distributors) to seize timing opportunities, particularly around certain countries where (s)VOD activities and platforms or hotly competing.
- Balance traditional and digital platforms, buyers and funders carefully in order to capture the cumulative and incremental revs in the nonexclusive deal sector, while also developing a longer term platform pipeline for future.
- Don’t stop at just one deal, unless exclusivity or funding elements are in play and worth it.
- Don’t be blocked per se by rights issues. Pragmatic business deals where others are “cut in” can help make those melt away
- Hybrid distribution: We as consultants/agents, aside from working direct for producers and platforms, now increasingly are retained by sales agents, distributors and even aggregators – as although they have the IP, they don’t always know all the others to sell to after going beyond the Big 5-7; this type of collaboration with producers and other reps on distribution yields good results (although time consuming at first) with each stakeholder getting a smaller piece but of a bigger pie. At the end of the day, 100% of zero is still zero.
- If not using a middleman at all, consider teaming up (especially if only selling a single film) with other producers to co-curate a mini-package of films around specific themes (e.g. eco, female, etc). This is particularly useful where the platforms don’t know you or your films, and it also helps program the service for their platform.
- Don’t abdicate distribution entirely to third parties, as in traditional past; now it is increasingly key to be aware of (if not participating more in) distribution and marketing (e.g. via social media). Help audiences know where to find your film!
Looking forward to seeing your films over here in EMEA!
Orly Ravid May 11th, 2016
Posted In: Amazon VOD & CreateSpace, book, case studies, Digital Distribution, Distribution, education, International Sales, iTunes, Netflix
Self financed Film Distribution in the Context of European Territories
 Last May, TFC released the second book in our series called Selling Your Film Outside the US. As with everything in the digital space, we are trying to keep track of a moving target. Netflix has now launched in France, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Belgium and Luxembourg. iTunes continues its transactional VOD domination by partnering with Middle East film distributor Front Row Filmed Entertainment to give Arabic and Bollywood films a chance to have simultaneous releases in eight countries: UAE, Egypt, Bahrain, Qatar, Oman, Lebanon, Jordan and Kuwait. Amazon has just launched several new original series in the US and UK, including critical darling Transparent, to a line up that includes returning series Alpha House and Betas.
Last May, TFC released the second book in our series called Selling Your Film Outside the US. As with everything in the digital space, we are trying to keep track of a moving target. Netflix has now launched in France, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Belgium and Luxembourg. iTunes continues its transactional VOD domination by partnering with Middle East film distributor Front Row Filmed Entertainment to give Arabic and Bollywood films a chance to have simultaneous releases in eight countries: UAE, Egypt, Bahrain, Qatar, Oman, Lebanon, Jordan and Kuwait. Amazon has just launched several new original series in the US and UK, including critical darling Transparent, to a line up that includes returning series Alpha House and Betas.
But what does DIY Distribution mean in the context of European territories? The following is an excerpt included in the book:
Here are a few tips for any filmmaker who is thinking about doing digital distribution in general, but especially in multiple territories:
-If your film is showing at an international film festival, ask if they are producing subtitles, and, if so, negotiate that the produced file be part of your festival fee. It may need to be proofed again or adjusted at a subtitling and transcription lab later on, but as a first pass it could prove very valuable down the road. See more about the kind of file you need in this post;
-When you are producing your master, create a textless version of your feature. Apple and probably other platforms will not allow external subtitles on any films that already have burn-ins. If your film, for example, has a few non-English lines of dialogue, instead of burning-in English subtitles into your film, a better method would be to create an external English-language subtitle file (separate from closed captioning) in a proper format and submit it with your master. Different aggregators may require different formats, and if you are going to a Captioning/Transcription/Translation Lab to do your closed captioning and subtitling work, be smart about which questions you ask and negotiate a price for everything, including transcoding from one format to another because you may not know exactly what you will need for all your deals right away.
Subtitles need to be timed to masters, so make sure your time code is consistent. When choosing a lab, ascertain whether they are capable of fulfilling all your current and future closed captioning and subtitling needs by verifying that they can output in the major formats, including (but not limited to) SubRip (.srt), SubViewer 1 & 2 (.sub), SubStation Alpha (.ssa/.ass), Spruce (.stl), Scenarist (.scc) and iTunes Timed Text (.itt);
-You may want to band together with films that are similar in theme or audience and shop your products around as bundled packages. Many digital services, including cable VOD, have thematic channels and your bundle of films may be more attractive as a package rather than just one film;
-Put the time in toward building your brand and your fanbase. Marketing still is the missing piece of the puzzle here. As it gets easier and easier to get onto platforms, so too does it get more difficult for audiences to find the films that are perfectly suited to their interests. This is especially true when talking about marketing one’s film outside one’s home territory. If you are accessing platforms for your film on your own, YOU are the distributor and the responsibility of marketing the film falls entirely to you.
To download a FREE copy of the entire book, complete with case studies of films distributed in Europe, visit sellingyourfilm.com.
Sheri Candler October 15th, 2014
Posted In: Amazon VOD & CreateSpace, book, case studies, Digital Distribution, DIY, iTunes, Netflix
Tags: Amazon, Digital Distribution, Europe, film bundles, independent film, iTunes, Middle East, Netflix, Selling Your Film Outside the US, Sheri Candler
All Stars of the Theatrical Self Release for Independent Films

Handling self funded theatrical distribution for TFC clients, I find myself wondering why more filmmakers don’t consider the self releasing option from a long-term career standpoint and the potential upside that comes from receiving the bulk of the revenue from the release. I am continually intrigued, pleased and surprised by the success of many who do.
Here are pristine recent examples of self funded releasing. These films each found specific ways to tap into their audience and often opted to do something outside the norm. For the sake of transparency I only am listing films that are admittedly self released in their approach. I would argue Middle of Nowhere is in fact a self funded release as it is a solid example of building and controlling a filmmaker’s brand, but I didn’t include it in this list.
While Gathr have a number of films that have done very well using their demand a screening platform (such as Anonymous People which TFC advised on), no TOD (theatrical on demand) release was as monumentally successful as Girl Rising. The film was aided by many factors such as funding from the Paul G. Allen Family Foundation, partnerships with Intel, the United Nations and World Vision as well as a small army of political and grassroots influencers, technologists and publicists. The documentary featured Hollywood A-list narrators like Meryl Streep, Anne Hathaway, Alicia Keys and Selena Gomez.and reached a fever pitch of screenings via the Gathr platform in the Spring of 2013. The film was also picked up by CNN Films for broadcast.
Much of the self funded distribution space is about the value of name recognition. Louis CK has such a loyal audience that he can get away with only selling his Live stand up docs on his website that are DRM free and asking fans not to upload it for free online. The films do so well that he is making seven figures in profit and will keep distributing them this way. His level of sales success, of course, is not realistic for most indie filmmakers, but it shows the value of brand developed over time. If you build up a loyal base and treat them with respect, they will follow you and as a result you can cut out the middle man.
Detropia world premiered at Sundance, won the editing award and came from two Oscar nominated directors. But they found distributors were wary to take on the film and/or didn’t get what the directors were trying to do. After a successful Kickstarter campaign to raise funds to self distribute, the film went on to gross over $300k+ theatrically. The filmmakers made the wise choice to open the film in a suburb of Detroit instead of NYC and the film grossed over $20k from that single screen at Landmark Royal Oak, far more than they would have launched with in NYC. They embraced their target audience and much like Escanaba in Da Moonlight pushed very heavily to a hometown crowd.
Sound City world premiered at Sundance 2013 and decided to do a day and date release less than a month after premiere. No distributor would have agreed to that. Dave Grohl himself promoted the film heavily (again the value of a fan base will pay off) and the film launched as the #1 doc on iTunes and grossed over $400k theatrically. It’s the highest grossing release from service theatrical company Variance to date. While fellow music recording doc Muscle Shoals may have grossed more money at the box office, they have to split the revenue with the distributor, Magnolia. Sound City likely made quite a bit more money back into their pockets.
Particle Fever has grossed over $850k to become the highest grossing Abramorama service release. They creatively tapped into the science community and quickly and quietly bypassed other more high profile docs like “Life Itself”. Using support from a community with solid internet leverage meant a lower P&A and this film, just shy of a $1 Mil grosser, can easily be called a success on all cylinders. It also doesn’t hurt that it scored a 95% from critics on Rotten Tomatoes. The film is now available for paid streaming on their website powered by VHX.
I Am Divine had a self funded theatrical release handled by The Film Collaborative. The film grossed $82k on a $8,000 release budget. This was run just as the film was finishing its 200+ festival screenings tour around the world for which the filmmaker has made 10’s of thousands from screening fees. We let social media and the Divine brand do much of the work as the colorful character inspired many around the world and they were excited to see his life story on the big screen. The film spent multiple weeks as the #1 Doc on ITunes when Wolfe Releasing put it out this year. A rare film to be profitable in every viewing arena.
God’s Not Dead again shows the value of a niche demographic that can be reached with the help of deep online data analysis. Working with Freestyle Releasing to open on 780 screens nationwide, the religious right pandering film has theatrically outgrossed Wes Anderson’s “The Grand Budapest Hotel,” which at its widest played over 1400 screens. This technically makes it the highest domestic grossing indie release this year. It’s passed $62 million on only a $2 Million budget production budget. The production worked with Ash Greyson’s Ribbow Media to handle a sizable social media advertising campaign directed toward Duck Dynasty, Kevin Sorbo, Dean Cain and Shane Harper fans and limited TV advertising on the 700 Club, Up TV and Pandora radio. It was a highly coordinated gamble that paid off handsomely. Lionsgate picked up the rights to distribute the movie through VOD (video on demand), SVOD (subscription video on demand) Pay-Per-View and television across the U.S. this month.
Upstream Color was the long awaited follow up from indie auteur Shane Carruth. He vetted offers while planning months in advance for a self funded release that launched out of the film’s Sundance premiere. Carefully planned and executed to reduce costs, Carruth’s intention was to give the film just enough of a theatrical release to legitimize and raise awareness for the film before sending it out to the online platforms where it would find actual significant revenue. For a while the film continued to play theaters simultaneously with the digital sales option, a feat almost unheard of in the Spring of 2013, but becoming a much more accepted and savvy practice now. Though lacking star wattage and a less than commercial story approach, Upstream Color amassed $444k and while Carruth kept full control of the release. The film is now widely available digitally.
Some honorary mentions for great self financed releases go to The Anonymous People (second highest grossing Gathr release despite no fest exposure), Spark: A Burning Man Story (Over $77k on another TOD service called TUGG with surcharged Burning Man tickets, over six figures theatrical and digital), Kids for Cash (Launched at 4 theaters in PA and grossed six figures), and Under the Electric Sky (a TUGG release with six figures, but curiously controlled by a traditional distributor, Focus Features).
Of this list, a vast number of the TOD releases are for documentary, some with star names attached and all with some kind of cause or niche audience interest to tap into and they all clearly did tap into that. Also, funds were raised to accomplish a theatrical release, hence the name self financed release. This should indicate to you that making a film meant for self funded release you NEED to have an identifiable brand, a social cause or a niche audience interest base to tap into. Think very carefully about how that film will be released successfully because these are the same considerations a distributor will look for when evaluating the release of a film.
Bryan Glick August 7th, 2014
Posted In: case studies, Distribution, DIY, Theatrical
Tags: Bryan Glick, Detropia, DIY film distribution, Gathr, Girl Rising, God's Not Dead, I am Divine, independent film, Kids for Cash, Particle Fever, Sound City, Spark: A Burning Man Story, The Anonymous People, The Film Collaborative, theatrical self release, Theatrical service company, Tugg, Under the Electric Sky, Upstream Color, Variance







